- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373929 > AD8027 (Analog Devices, Inc.) Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | AD8027 |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices, Inc. |
| 元件分類: | 運動控制電子 |
| 英文描述: | Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers |
| 中文描述: | 低失真,高速軌到軌輸入/輸出放大器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 16/24頁 |
| 文件大小: | 478K |
| 代理商: | AD8027 |
AD8027/AD8028
THEORY OF OPERATION
The AD8027/AD8028 is a rail-to-rail input and output amplifier
designed in Analog Devices XFCB process. The XFCB process
enables the AD8027/AD8028 to run on 2.7 V to 12 V supplies
with 190 MHz of bandwidth and over 100 V/μs of slew rate. The
AD8027/AD8028 has 4.3 nV/√Hz of wideband noise with
17 nV/√Hz noise at 10 Hz. This noise performance, with an
offset and drift performance of less than 900 μV maximum and
1.5 μV/°C typical, respectively, makes the AD8027/AD8028
ideal for high speed precision applications. Additionally, the
input stage operates 200 mV beyond the supply rails and shows
no phase reversal. The amplifier features overvoltage protection
on the input stage. Once the inputs exceed the supply rails by
0.7 V, ESD protection diodes will turn on, drawing excessive
current through the differential input pins. A series input resis-
tor should be included to limit the input current to less than
10 mA.
Rev. B | Page 16 of 24
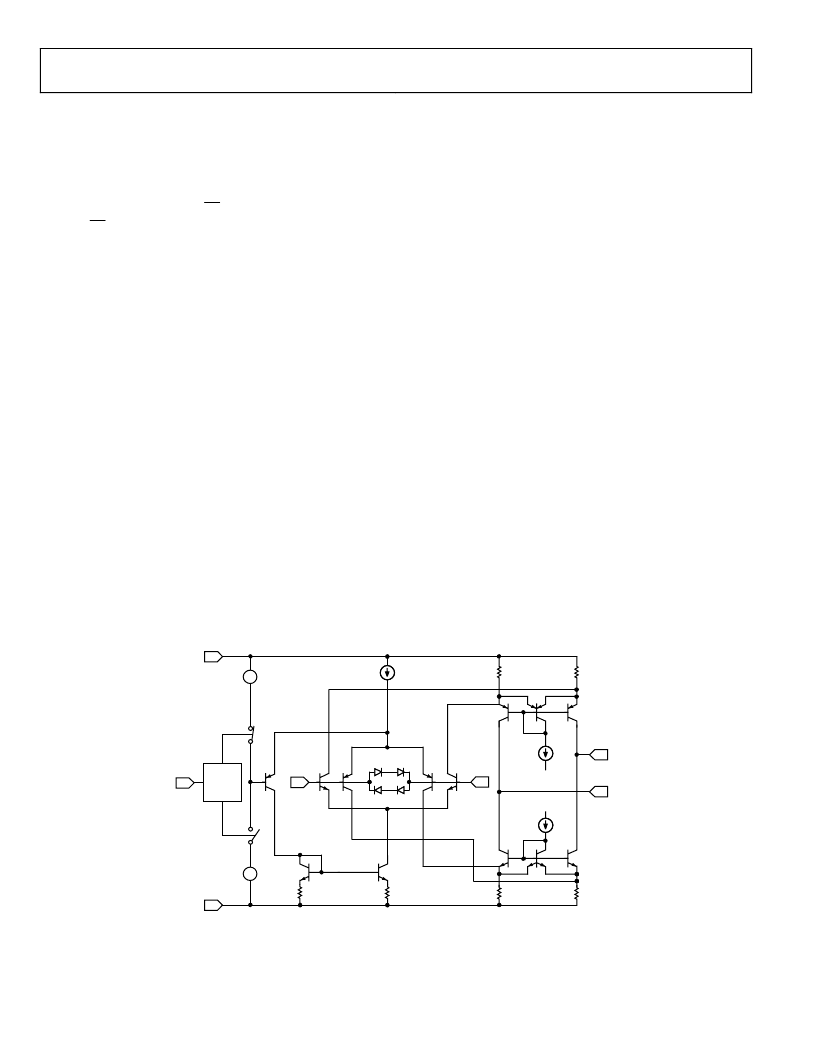
Input Stage
The rail-to-rail input performance is achieved by operating
complementary input pairs. Which pair is on is determined by
the common-mode level of the differential input signal. Look-
ing at the schematic in Figure 55, a tail current (I
TAIL
) is gener-
ated that sources the PNP differential input structure consisting
of Q1 and Q2. A reference voltage is generated internally that is
connected to the base of Q5. This voltage is continually com-
pared against the common-mode input voltage. When the
common-mode level exceeds the internal reference voltage, Q5
diverts the tail current (I
TAIL
) from the PNP input pair to a cur-
rent mirror that sources the NPN input pair consisting of Q3
and Q4. The NPN input pair can now operate 200 mV above
the positive rail. Both input pairs are protected from differential
input signals above 1.4 V by four diodes across the input (see
Figure 55). In the event of differential input signals that exceed
1.4 V, the diodes will conduct and excessive current will flow
through them. A series input resistor should be included to limit
the input current to 10 mA.
Crossover Selection
A new feature available on the AD8027/AD8028, which is called
Crossover Selection, allows the user to choose the crossover
point between the PNP/NPN differential pairs. Although the
crossover region is small, operating in this region should be
avoided since it can introduce offset and distortion to the out-
put signal. To help avoid operating in the crossover region, the
AD8027/AD8028 allows the user to select from two preset
crossover locations (i.e., voltage levels) using the SELECT pin.
Looking at the schematic in Figure 55, the crossover region is
about 200 mV and is defined by the voltage level at the base of
Q5. Internally, two separate voltage sources are created approxi-
mately 1.2 V from either rail. One or the other is connected to
Q5 based on the voltage applied to the SELECT pin. This allows
for either dominant PNP pair operation, when the SELECT pin
is left open, or dominant NPN pair operation, when the
SELECT pin is pulled high. This pin also provides the tradi-
tional power-down function when it is pulled low. This allows
the designer to achieve the best precision and ac performance
for high-side and low-side signal applications. See Figure 50
through Figure 53 for SELECT pin characteristics.
VCC
1.2V
+
–
VEE
I
TAIL
1.2V
+
–
LOGIC
VSEL
VP
Q5
Q3
Q1
Q2
Q4
VN
VOUTP
VOUTN
I
CMFB
VCC
VEE
I
CMFB
03327-A-054
Figure 55. Simplified Input Stage
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD8027AR | Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers |
| AD8027AR-REEL | Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers |
| AD8027AR-REEL7 | Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers |
| AD8027ART-R2 | Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers |
| AD8027ART-REEL | Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| AD8027_05 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:Low Distortion, High Speed Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Amplifiers |
| AD8027AR | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:OP Amp Single GP R-R I/O 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:IC OP-AMP LOW POWER |
| AD8027AR-EBZ | 功能描述:BOARD EVAL FOR AD8027AR RoHS:是 類別:編程器,開發(fā)系統(tǒng) >> 評估板 - 運算放大器 系列:- 產品培訓模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標準包裝:1 系列:- |
| AD8027AR-REEL | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:OP Amp Single GP R-R I/O 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:SOIC, SINGLE LOW-PWR VLTG-FDBK OP AMP - Tape and Reel |
| AD8027AR-REEL7 | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:OP Amp Single GP R-R I/O 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:OP Amp Single GP R-R I/O ±6V/12V 8-Pin SOIC N T/R 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:HIGH SPEED, RAIL-TO-RAIL IN/OUT OP-AMP - Tape and Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。