- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄30743 > LM1575J-CAD/883 (NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) 3.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 62 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, CDIP16 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | LM1575J-CAD/883 |
| 廠商: | NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | 3.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 62 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, CDIP16 |
| 封裝: | CERDIP-16 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/30頁 |
| 文件大小: | 676K |
| 代理商: | LM1575J-CAD/883 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁當(dāng)前第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁
Application Hints (Continued)
of printed circuit board copper, such as a ground plane.
Large areas of copper provide the best transfer of heat to the
surrounding air. Copper on both sides of the board is also
helpful in getting the heat away from the package, even if
there is no direct copper contact between the two sides.
Thermal resistance numbers as low as 40C/W for the SO
package, and 30C/W for the N package can be realized with
a carefully engineered pc board.
Included on the
Switchers Made Simple design software is
a more precise (non-linear) thermal model that can be used
to determine junction temperature with different input-output
parameters or different component values. It can also calcu-
late the heat sink thermal resistance required to maintain the
regulators junction temperature below the maximum operat-
ing temperature.
Additional Applications
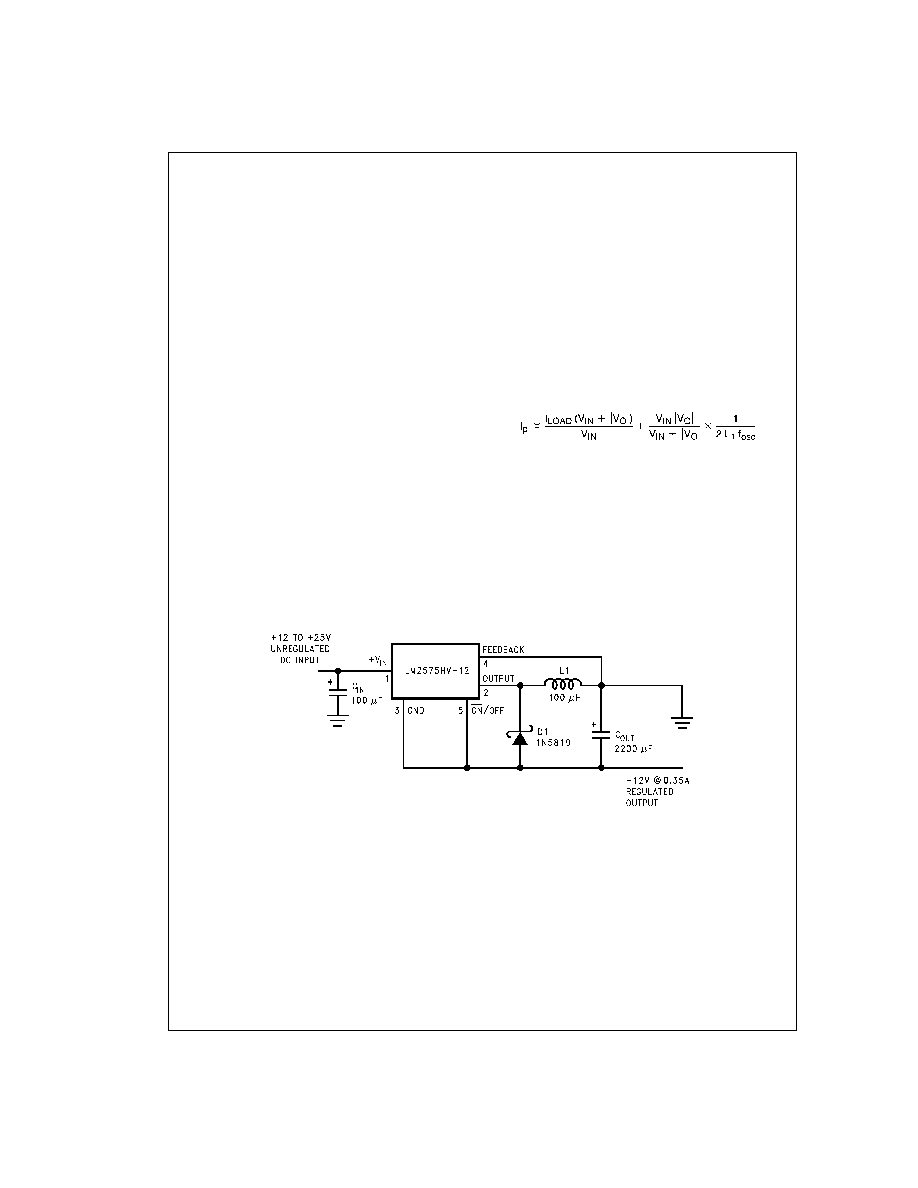
INVERTING REGULATOR
Figure 10 shows a LM2575-12 in a buck-boost configuration
to generate a negative 12V output from a positive input volt-
age. This circuit bootstraps the regulator’s ground pin to the
negative output voltage, then by grounding the feedback pin,
the regulator senses the inverted output voltage and regu-
lates it to 12V.
For an input voltage of 12V or more, the maximum available
output current in this configuration is approximately 0.35A. At
lighter loads, the minimum input voltage required drops to
approximately 4.7V.
The switch currents in this buck-boost configuration are
higher than in the standard buck-mode design, thus lowering
the available output current. Also, the start-up input current
of the buck-boost converter is higher than the standard
buck-mode regulator, and this may overload an input power
source with a current limit less than 1.5A. Using a delayed
turn-on or an undervoltage lockout circuit (described in the
next section) would allow the input voltage to rise to a high
enough level before the switcher would be allowed to turn
on.
Because of the structural differences between the buck and
the buck-boost regulator topologies, the buck regulator de-
sign procedure section can not be used to to select the in-
ductor or the output capacitor. The recommended range of
inductor values for the buck-boost design is between 68 H
and 220 H, and the output capacitor values must be larger
than what is normally required for buck designs. Low input
voltages or high output currents require a large value output
capacitor (in the thousands of micro Farads).
The peak inductor current, which is the same as the peak
switch current, can be calculated from the following formula:
Where f
osc = 52 kHz. Under normal continuous inductor cur-
rent operating conditions, the minimum V
IN represents the
worst case. Select an inductor that is rated for the peak cur-
rent anticipated.
Also, the maximum voltage appearing across the regulator is
the absolute sum of the input and output voltage. For a 12V
output, the maximum input voltage for the LM2575 is +28V,
or +48V for the LM2575HV.
The
Switchers Made Simple (version 3.3) design software
can be used to determine the feasibility of regulator designs
using different topologies, different input-output parameters,
different components, etc.
NEGATIVE BOOST REGULATOR
Another variation on the buck-boost topology is the negative
boost configuration. The circuit in
Figure 11 accepts an input
voltage ranging from 5V to 12V and provides a regulated
12V output. Input voltages greater than 12V will cause the
output to rise above 12V, but will not damage the regulator.
Because of the boosting function of this type of regulator, the
switch current is relatively high, especially at low input volt-
ages. Output load current limitations are a result of the maxi-
mum current rating of the switch. Also, boost regulators can
not provide current limiting load protection in the event of a
shorted load, so some other means (such as a fuse) may be
necessary.
DS011475-15
FIGURE 10. Inverting Buck-Boost Develops 12V
www.national.com
18
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LMX2575MX-15 | 3.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 63 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO24 |
| LMX2575MX-5.0 | 3.2 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 63 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO24 |
| LM1576-5.0AK | 3.5 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 52 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, MBFM2 |
| LM1576-12AK | 3.5 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 52 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, MBFM2 |
| LM1596H/883 | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, MBCY10 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LM1575K-12 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Voltage-Mode SMPS Controller |
| LM1575K-12/883 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Voltage-Mode SMPS Controller |
| LM1575K-12/883C | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| LM1575K-12/883QF | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| LM1575K-12-QML | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:SIMPLE SWITCHER 1A STEP-DOWN VOLTAGE REGULATOR |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。