- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > Datasheet目錄42 > LTC4263IS#TRPBF (Linear Technology)IC IEEE 803.2AF CNTRLR 14-SOIC Datasheet資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | LTC4263IS#TRPBF |
| 廠商: | Linear Technology |
| 文件頁數: | 11/24頁 |
| 文件大小: | 354K |
| 描述: | IC IEEE 803.2AF CNTRLR 14-SOIC |
| 標準包裝: | 2,500 |
| 類型: | 以太網供電(PoE) |
| 應用: | 用于以太網供電(PoE)設備的電源接口開關 |
| 電源電壓: | 48V |
| 工作溫度: | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 封裝/外殼: | 14-SOIC(0.154",3.90mm 寬) |
| 供應商設備封裝: | 14-SOIC |
| 包裝: | 帶卷 (TR) |
LTC4263
11
4263fe
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
LTC4263 OPERATION
Signature Detection
The IEEE 802.3af speci cation de nes a speci c pair-to-
pair signature resistance used to identify a device that
can accept power via its Ethernet connection. When the
port voltage is below 10V , an IEEE 802.3af compliant
PD will have an input resistance of approximately 25k?
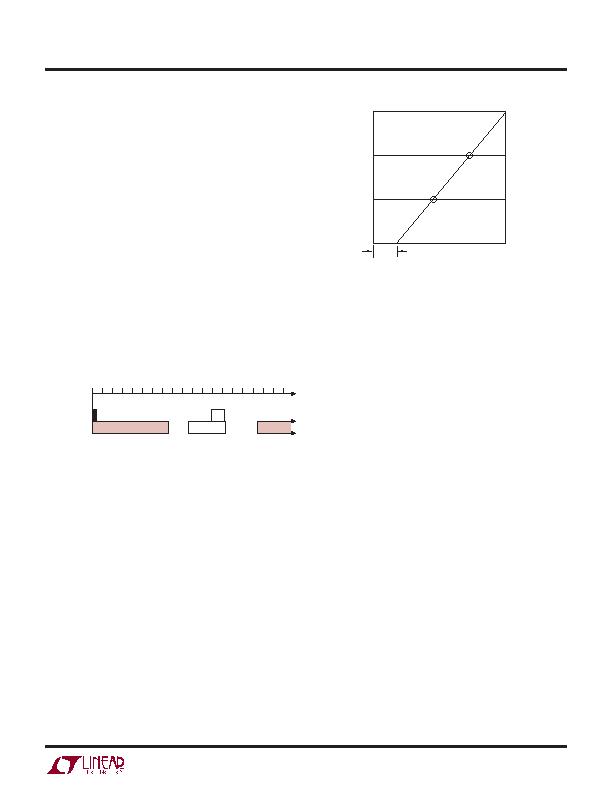
Figure 2 illustrates the relationship between the PD sig-
nature resistance and the required resistance ranges the
PSE must accept and reject. According to the IEEE 802.3af
speci cation, the PSE must accept PDs with signatures
between 19k?and 26.5k?and may or may not accept
resistances in the two ranges of 15k?to 19k?and 26.5k?
to 33k? The black box in Figure 2 represents the typical
150?pair-to-pair termination used in Ethernet devices
like a computers network interface card (NIC) that cannot
accept power.
The LTC4263 checks for the signature resistance by forcing
two test currents on the port in sequence and measuring
the resulting voltages. It then subtracts the two V-I points
to determine the resistive slope while removing voltage
offset caused by any series diodes or current offset caused
by leakage at the port (see Figure 3). The LTC4263 will
typically accept any PD resistance between 17k?and
29.7k?as a valid PD. Values outside this range (exclud-
ing open and short-circuits) are reported to the user by a
code ashed via the LED pin.
The LTC4263 uses a force-current detection method in
order to reduce noise sensitivity and provide a more robust
detection algorithm. The rst test point is taken by forcing
a test current into the port, waiting a short time to allow
the line to settle and measuring the resulting voltage. This
result is stored and the second current is applied to the
port, allowed to settle and the voltage measured.
The LTC4263 will not power the port if the PD has more
than 5糉 in parallel with its signature resistor unless legacy
mode is enabled.
The LTC4263 autonomously tests for a valid PD connected
to the port. It repeatedly queries the port every 580ms, or
every 3.2s if midspan backoff mode is active (see below).
If detection is successful, it performs classi cation and
power management and then powers up the port.
Midspan Backoff
IEEE 802.3af requires the midspan PSE to wait two seconds
after a failed detection before attempting to detect again
unless the port resistance is greater than 500k? This
requirement is to prevent the condition of an endpoint PSE
and a midspan PSE, connected to the same PD at the same
time, from each corrupting the PD signature and preventing
power-on. After the rst corrupted detection cycle, the
midspan PSE waits while the endpoint PSE completes
detection and turns the port on. If the midspan mode of
the LTC4263 is enabled by connecting the MIDSPAN pin to
V
DD5
, a 3.2 second delay occurs after every failed detect
cycle unless the result is an open circuit.
Figure 2. IEEE 802.3af Signature Resistance Ranges
Figure 3. PD 2-Point Detection
RESISTANCE
PD
PSE
0?/DIV>
10k
15k
4263 F02
19k
26.5k
26.25k
23.75k
150?(NIC)
20k
30k
33k
REJECT
ACCEPT
REJECT
FIRST
DETECTION
POINT
SECOND
DETECTION
POINT
VALID PD
25k?SLOPE
255
180
0V-2V
OFFSET
VOLTAGE
4263 F03
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LTC4268IDKD-1#PBF | IC PD HIGH POWER W/CNTRL 32-DFN |
| LTC4274CUHF#PBF | IC CONTROLLER POE 38-QFN |
| LTC4280CUFD#PBF | IC CONTROLLER HOT SWAP QFN-24 |
| LTC4300-1IMS8#TRPBF | IC HOTSWAP 2WIRE BUS BUFFR 8MSOP |
| LTC4300A-2IMS8#TRPBF | IC BUFFER BUS 2WR HOTSWAP 8-MSOP |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| LTC4264 | 制造商:LINER 制造商全稱:Linear Technology 功能描述:Synchronous No-Opto Flyback Controller |
| LTC4264CDE | 制造商:LINER 制造商全稱:Linear Technology 功能描述:High Power PD Interface Controller with 750mA Current Limit |
| LTC4264CDE#PBF | 功能描述:IC CNTRLR PD INTERFACE 12-DFN RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 接口 - 控制器 系列:- 標準包裝:2,450 系列:- 控制器類型:SPI 總線至 I²C 總線橋接 接口:I²C,串行,SPI 電源電壓:2.4 V ~ 3.6 V 電流 - 電源:11mA 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:24-VFQFN 裸露焊盤 供應商設備封裝:24-HVQFN(4x4) 包裝:托盤 配用:568-3511-ND - DEMO BOARD SPI TO I2C 其它名稱:935286452157SC18IS600IBSSC18IS600IBS-ND |
| LTC4264CDE#TRPBF | 功能描述:IC INTERFACE 802.3AT 12-DFN RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 接口 - 控制器 系列:- 標準包裝:2,450 系列:- 控制器類型:SPI 總線至 I²C 總線橋接 接口:I²C,串行,SPI 電源電壓:2.4 V ~ 3.6 V 電流 - 電源:11mA 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:24-VFQFN 裸露焊盤 供應商設備封裝:24-HVQFN(4x4) 包裝:托盤 配用:568-3511-ND - DEMO BOARD SPI TO I2C 其它名稱:935286452157SC18IS600IBSSC18IS600IBS-ND |
| LTC4264IDE | 制造商:LINER 制造商全稱:Linear Technology 功能描述:High Power PD Interface Controller with 750mA Current Limit |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。