- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄98034 > MPSA92RL (ON SEMICONDUCTOR) 500 mA, 300 V, PNP, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | MPSA92RL |
| 廠商: | ON SEMICONDUCTOR |
| 元件分類: | 小信號晶體管 |
| 英文描述: | 500 mA, 300 V, PNP, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, TO-226AA, 3 PIN |
| 文件頁數: | 24/34頁 |
| 文件大小: | 320K |
| 代理商: | MPSA92RL |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁當前第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁
Reliability and Quality Assurance
9–18
Motorola Small–Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Device Data
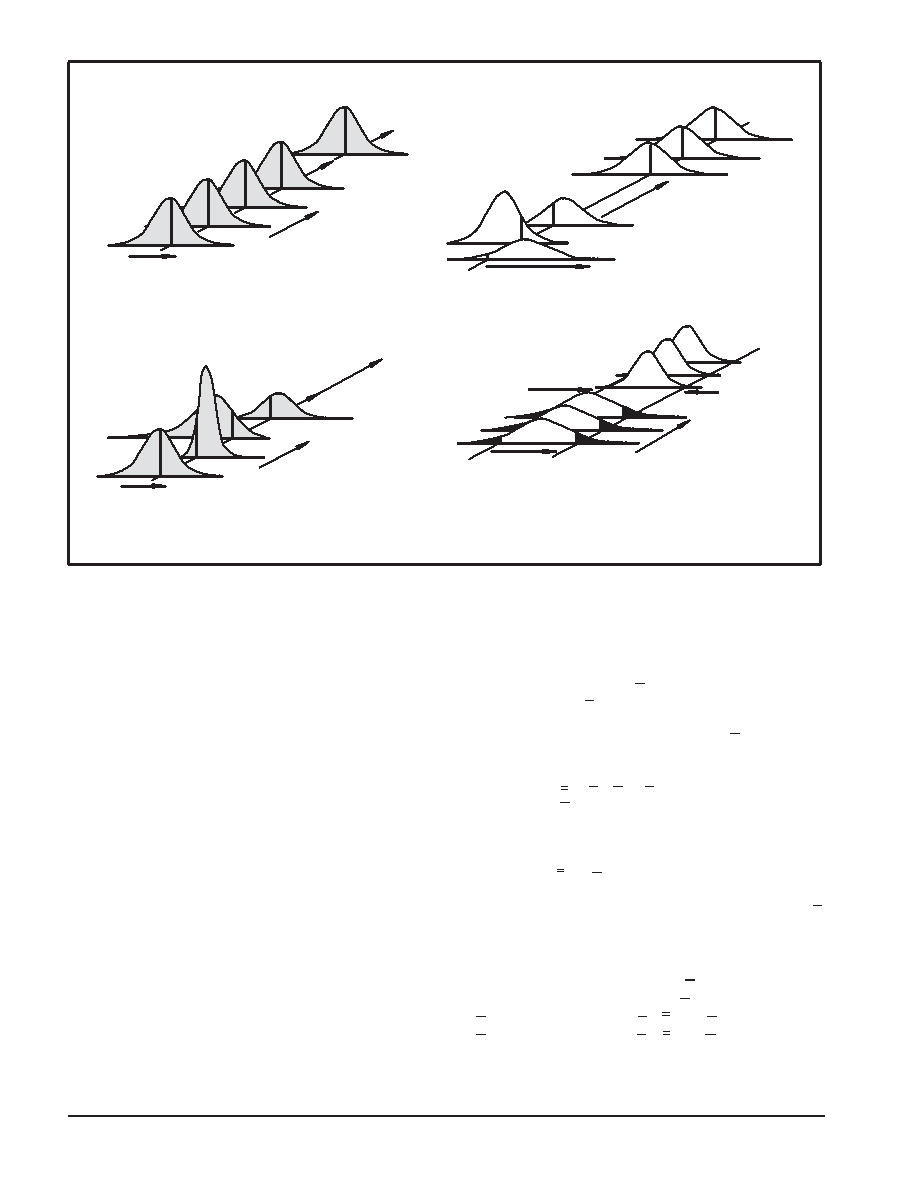
Figure 2. Impact of Assignable Causes
on Process Predictable
Figure 3. Difference Between Process
Control and Process Capability
?
Process “under control” – all assignable causes are
removed and future distribution is predictable.
PREDICTION
TIME
SIZE
TIME
PREDICTION
SIZE
TIME
Out of control
(assignable causes present)
In control assignable
causes eliminated
SIZE
TIME
In control but not capable
(variation from random variability
excessive)
Lower
Specification Limit
Upper
Specification Limit
In control and capable
(variation from random
variability reduced)
?
At Motorola, for critical parameters, the process capability
is acceptable with a Cpk = 1.50 with continual improvement
our goal. The desired process capability is a Cpk = 2 and the
ideal is a Cpk = 5. Cpk, by definition, shows where the current
production process fits with relationship to the specification
limits. Off center distributions or excessive process variability
will result in less than optimum conditions.
SPC IMPLEMENTATION AND USE
CPSTG uses many parameters that show conformance to
specification. Some parameters are sensitive to process
variations while others remain constant for a given product
line. Often, specific parameters are influenced when changes
to other parameters occur. It is both impractical and
unnecessary to monitor all parameters using SPC methods.
Only critical parameters that are sensitive to process
variability are chosen for SPC monitoring. The process steps
affecting these critical parameters must be identified as well.
It is equally important to find a measurement in these process
steps that correlates with product performance. This
measurement is called a critical process parameter.
Once the critical process parameters are selected, a
sample plan must be determined. The samples used for
measurement are organized into RATIONAL SUBGROUPS
of approximately two to five pieces. The subgroup size should
be such that variation among the samples within the subgroup
remain small. All samples must come from the same source
e.g., the same mold press operator, etc. Subgroup data should
be collected at appropriate time intervals to detect variations
in the process. As the process begins to show improved
stability, the interval may be increased. The data collected
must be carefully documented and maintained for later
correlation. Examples of common documentation entries are
operator, machine, time, settings, product type, etc.
Once the plan is established, data collection may begin. The
data collected with generate X and R values that are plotted
with respect to time. X refers to the mean of the values within
a given subgroup, while R is the range or greatest value minus
least value. When approximately 20 or more X and R values
have been generated, the average of these values is
computed as follows:
X = (X + X2 + X3 + . . .)/K
R = (R1 + R2 + R2 + . . .)/K
where K = the number of subgroups measured.
The values of X and R are used to create the process control
chart. Control charts are the primary SPC tool used to signal
a problem. Shown in Figure 4, process control charts show X
and R values with respect to time and concerning reference
to upper and lower control limit values. Control limits are
computed as follows:
R upper control limit = UCLR = D4 R
R lower control limit = LCLR = D3 R
X upper control limit = UCLX = X + A2 R
X lower control limit = LCL X = X – A2 R
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MPSA93RL | 500 mA, 200 V, PNP, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| MPSA93RLRE | 500 mA, 200 V, PNP, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| MPSA93RL1 | 500 mA, 200 V, PNP, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| MPSH10L34Z | UHF BAND, Si, NPN, RF SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR |
| MPSH10J18Z | UHF BAND, Si, NPN, RF SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| MPSA92RL1 | 功能描述:兩極晶體管 - BJT 500mA 300V PNP RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 配置: 晶體管極性:PNP 集電極—基極電壓 VCBO: 集電極—發射極最大電壓 VCEO:- 40 V 發射極 - 基極電壓 VEBO:- 6 V 集電極—射極飽和電壓: 最大直流電集電極電流: 增益帶寬產品fT: 直流集電極/Base Gain hfe Min:100 A 最大工作溫度: 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:PowerFLAT 2 x 2 |
| MPSA92RL1G | 功能描述:兩極晶體管 - BJT 500mA 300V PNP RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 配置: 晶體管極性:PNP 集電極—基極電壓 VCBO: 集電極—發射極最大電壓 VCEO:- 40 V 發射極 - 基極電壓 VEBO:- 6 V 集電極—射極飽和電壓: 最大直流電集電極電流: 增益帶寬產品fT: 直流集電極/Base Gain hfe Min:100 A 最大工作溫度: 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:PowerFLAT 2 x 2 |
| MPSA92RLRA | 功能描述:兩極晶體管 - BJT 500mA 300V PNP RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 配置: 晶體管極性:PNP 集電極—基極電壓 VCBO: 集電極—發射極最大電壓 VCEO:- 40 V 發射極 - 基極電壓 VEBO:- 6 V 集電極—射極飽和電壓: 最大直流電集電極電流: 增益帶寬產品fT: 直流集電極/Base Gain hfe Min:100 A 最大工作溫度: 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:PowerFLAT 2 x 2 |
| MPSA92RLRAG | 功能描述:兩極晶體管 - BJT 500mA 300V PNP RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 配置: 晶體管極性:PNP 集電極—基極電壓 VCBO: 集電極—發射極最大電壓 VCEO:- 40 V 發射極 - 基極電壓 VEBO:- 6 V 集電極—射極飽和電壓: 最大直流電集電極電流: 增益帶寬產品fT: 直流集電極/Base Gain hfe Min:100 A 最大工作溫度: 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:PowerFLAT 2 x 2 |
| MPSA92RLRM | 功能描述:兩極晶體管 - BJT 500mA 300V PNP RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 配置: 晶體管極性:PNP 集電極—基極電壓 VCBO: 集電極—發射極最大電壓 VCEO:- 40 V 發射極 - 基極電壓 VEBO:- 6 V 集電極—射極飽和電壓: 最大直流電集電極電流: 增益帶寬產品fT: 直流集電極/Base Gain hfe Min:100 A 最大工作溫度: 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:PowerFLAT 2 x 2 |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。