- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373920 > AD7854BR (ANALOG DEVICES INC) 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 12-Bit Sampling ADCs PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | AD7854BR |
| 廠商: | ANALOG DEVICES INC |
| 元件分類: | ADC |
| 英文描述: | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 12-Bit Sampling ADCs |
| 中文描述: | 1-CH 12-BIT SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC, PARALLEL ACCESS, PDSO28 |
| 封裝: | SOIC-28 |
| 文件頁數: | 16/28頁 |
| 文件大小: | 264K |
| 代理商: | AD7854BR |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁當前第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁
AD7854/AD7854L
–
16
–
REV. B
REFERENCE SECTION
For specified performance, it is recommended that when using
an external reference, this reference should be between 2.3 V
and the analog supply AV
DD
. The connections for the reference
pins are shown below. If the internal reference is being used,
the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin should be decoupled with a 100 nF
capacitor to AGND very close to the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin. These
connections are shown in Figure 16.
If the internal reference is required for use external to the ADC,
it should be buffered at the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin and a 100 nF
capacitor should be connected from this pin to AGND. The typical
noise performance for the internal reference, with 5V supplies is
150 nV/
√
Hz
@ 1 kHz and dc noise is 100
μ
V p-p.
AV
DD
DV
DD
C
REF1
C
REF2
REF
IN
/REF
OUT
AD7854/
AD7854L
ANALOG
SUPPLY
+3V TO +5V
0.1 F
0.1 F
10 F
0.1 F
0.01 F
0.1 F
Figure 16. Relevant Connections Using Internal Reference
The REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin may be overdriven by connecting it to
an external reference. This is possible due to the series resis-
tance from the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin to the internal reference.
This external reference can be in the range 2.3 V to AV
DD
.
When using AV
DD
as the reference source, the 10 nF capacitor
from the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin to AGND should be as close as
possible to the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin, and also the C
REF1
pin
should be connected to AV
DD
to keep this pin at the same volt-
age as the reference. The connections for this arrangement are
shown in Figure 17. When using AV
DD
it may be necessary to
add a resistor in series with the AV
DD
supply. This has the effect
of filtering the noise associated with the AV
DD
supply.
Note that when using an external reference, the voltage present
at the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin is determined by the external refer-
ence source resistance and the series resistance of 150 k
from
the REF
IN
/REF
OUT
pin to the internal 2.5 V reference. Thus, a
low source impedance external reference is recommended.
AV
DD
DV
DD
C
REF1
C
REF2
REF
IN
/REF
OUT
AD7854/
AD7854L
ANALOG
SUPPLY
+3V TO +5V
0.1 F
0.1 F
10 F
0.1 F
0.01 F
0.01 F
Figure 17. Relevant Connections, AV
DD
as the Reference
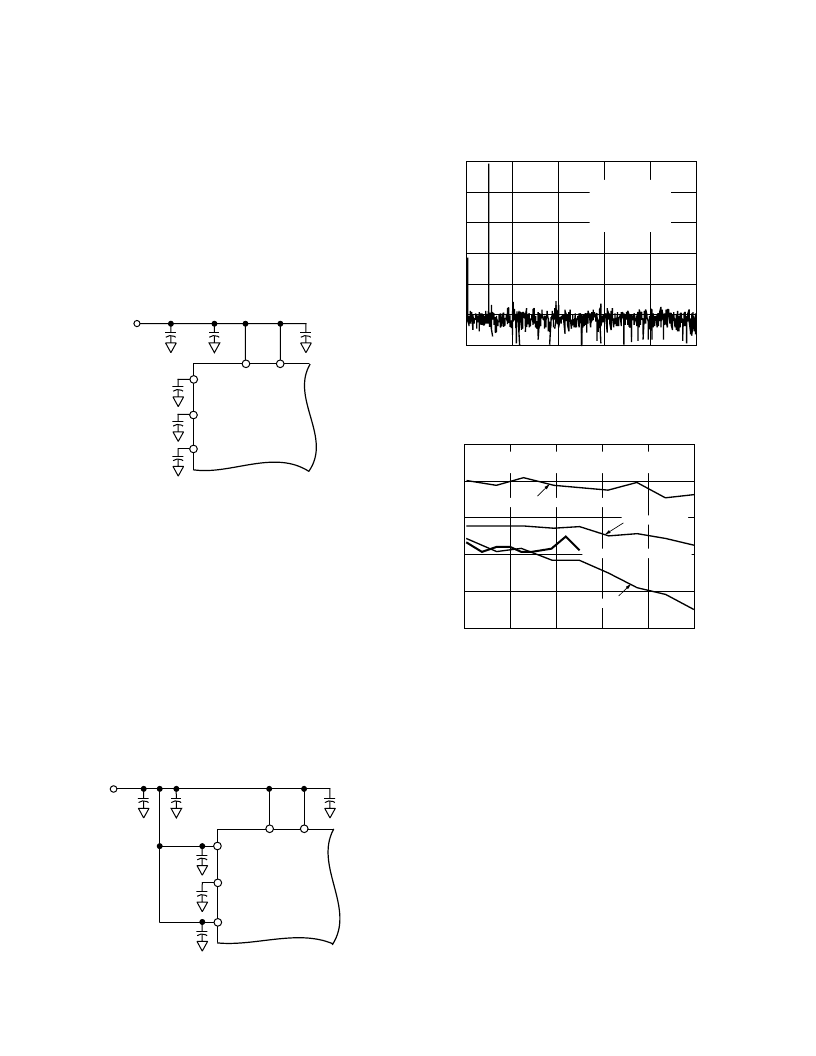
AD7854/AD7854L PERFORMANCE CURVES
Figure 18 shows a typical FFT plot for the AD7854 at 200 kHz
sample rate and 10 kHz input frequency.
FREQUENCY
–
kHz
0
–
20
–
1200
100
20
S
–
40
60
–
40
–
60
–
80
80
–
100
AV
DD
= DV
DD
= 3.3V
F
SAMPLE
= 200kHz
F
SNR = 72.04dB
THD =
–
88.43dB
Figure 18. FFT Plot
Figure 19 shows the SNR versus frequency for different supplies
and different external references.
INPUT FREQUENCY
–
kHz
74
73
690
100
20
S
–
40
80
72
71
70
60
AV
DD
= DV
WITH 2.5V REFERENCE
UNLESS STATED OTHERWISE
5.0V SUPPLIES, WITH 5V REFERENCE
5.0V SUPPLIES
5.0V SUPPLIES, L VERSION
3.3V SUPPLIES
Figure 19. SNR vs. Frequency
Figure 20 shows the power supply rejection ratio versus fre-
quency for the part. The power supply rejection ratio is defined
as the ratio of the power in ADC output at frequency f to the
power of a full-scale sine wave:
PSRR (dB) =
10
log (Pf/Pfs)
Pf
= Power at frequency f in ADC output,
Pfs
= power of a full-
scale sine wave. Here a 100 mV peak-to-peak sine wave is
coupled onto the AV
DD
supply while the digital supply is left
unaltered. Both the 3.3 V and 5.0 V supply performances are
shown.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7854AR | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 12-Bit Sampling ADCs |
| AD7854L | 12-Bit Sampling ADC(單電源,200kSPS 12位采樣A/D轉換器) |
| AD7854 | 12-Bit Sampling ADC(單電源,200kSPS 12位采樣A/D轉換器) |
| AD7858LARS | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC |
| AD7858BN | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7854BR-REEL | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:ADC Single SAR 200ksps 12-bit Parallel 28-Pin SOIC W T/R |
| AD7854BRZ | 功能描述:IC ADC 12BIT PARALLEL LP 28-SOIC RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 數據采集 - 模數轉換器 系列:- 產品培訓模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標準包裝:2,500 系列:- 位數:12 采樣率(每秒):3M 數據接口:- 轉換器數目:- 功率耗散(最大):- 電壓電源:- 工作溫度:- 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:SOT-23-6 供應商設備封裝:SOT-23-6 包裝:帶卷 (TR) 輸入數目和類型:- |
| AD7854L | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 12-Bit Sampling ADCs |
| AD7854LAQ | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:12 BIT SINGLE CHANNEL PARALLEL ADC I.C. - Bulk |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。