- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373951 > AD8608 (Analog Devices, Inc.) Precision Low noise CMOS Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifiers PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | AD8608 |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | Precision Low noise CMOS Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifiers |
| 中文描述: | 精密低噪聲CMOS軌到軌輸入/輸出運算放大器 |
| 文件頁數: | 16/20頁 |
| 文件大小: | 559K |
| 代理商: | AD8608 |
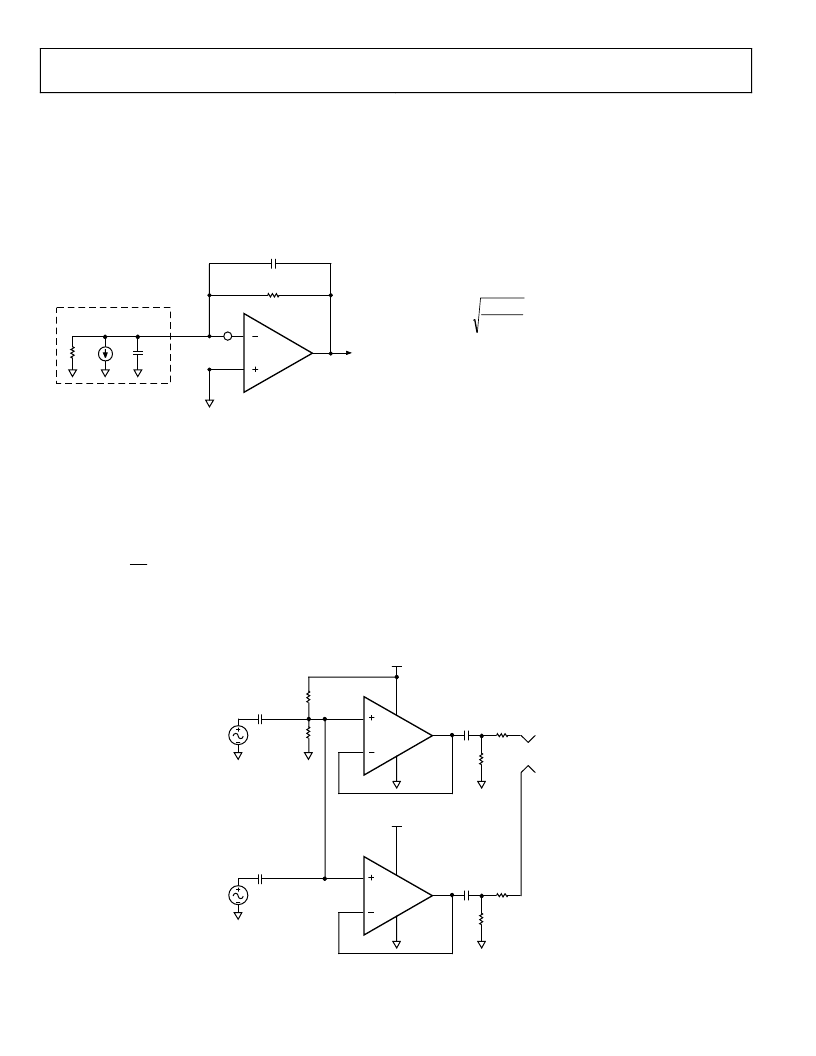
AD8605/AD8606/AD8608
I-V CONVERSION APPLICATIONS
PHOTODIODE PREAMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS
The low offset voltage and input current of the AD8605 make it
an excellent choice for photodiode applications. In addition, the
low voltage and current noise make the amplifier ideal for
application circuits with high sensitivity.
Rev. D | Page 16 of 20
R
D
I
D
C
50pF
AD8605
V
OUT
PHOTODIODE
+VOS–
R
F
10M
C
F
10pF
0
Figure 51. Equivalent Circuit for Photodiode Preamp
The input bias current of the amplifier contributes an error
term that is proportional to the value of R
F
.
The offset voltage causes a dark current induced by the shunt
resistance of the diode
R
D
. These error terms are combined at
the output of the amplifier. The error voltage is written as
B
F
D
F
OS
O
I
R
R
R
V
E
+
+
=
1
Typically,
R
F
is smaller than
R
D
, thus
R
F
/
R
D
can be ignored.
At room temperature, the AD8605 has an input bias current of
0.2 pA and an offset voltage of 100 μV. Typical values of R
D
are
in the range of 1 G.
For the circuit shown in Figure 9, the output error voltage is
approximately 100 μV at room temperature, increasing to about
1 mV at 85°C.
Where
f
t
is the unity gain frequency of the amplifier, the
maximum achievable signal bandwidth is
T
F
t
MAX
C
R
f
f
π
=
2
AUDIO AND PDA APPLICATIONS
The AD8605’s low distortion and wide dynamic range make it a
great choice for audio and PDA applications, including
microphone amplification and line output buffering.
Figure 52 shows a typical application circuit for headphone/line
out amplification.
R1 and R2 are used to bias the input voltage at half the supply.
This maximizes the signal bandwidth range. C1 and C2 are used
to ac couple the input signal. C1 and R2 form a high-pass filter
whose corner frequency is 1/2πR1C1.
The high output current of the AD8605 allows it to drive heavy
resistive loads.
The circuit of Figure 52 was tested to drive a 16 W headphone.
The THD + N is maintained at approximately 60 dB
throughout the audio range.
5V
4
2
3
8
1
HEADPHONES
5V
4
6
5
8
7
C1
1
μ
F
R1
10k
R2
10k
V1
500mV
1/2
AD8606
C3
100
μ
F
R4
20
R3
1k
1/2
AD8606
C4
100
μ
F
R6
20
R5
1k
C2
1
μ
F
V2
500mV
0
Figure 52. Single-Supply Headphone/Speaker Amplifier
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD8608AR | Precision Low noise CMOS Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifiers |
| AD8608ARU | Precision Low noise CMOS Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifiers |
| AD8605ART-REEL | Precision Low noise CMOS Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifiers |
| AD8605ART-REEL7 | Precision Low noise CMOS Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifiers |
| AD8605ARTZ-REEL | Precision Low noise CMOS Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifiers |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| AD8608_CN | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:精密、低噪聲、CMOS軌到軌輸入/輸出運算放大器 |
| AD8608AR | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:IC OP-AMP QUAD R/R |
| AD8608ARN | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Operational Amplifier |
| AD8608AR-REEL | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:OP Amp Quad GP R-R I/O 5.5V 14-Pin SOIC N T/R |
| AD8608AR-REEL7 | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:OP Amp Quad GP R-R I/O 5.5V 14-Pin SOIC N T/R |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。