- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄18702 > EFM32-TG230F32-SK (Energy Micro)IC MICRO KIT GECKO 64QFN PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | EFM32-TG230F32-SK |
| 廠商: | Energy Micro |
| 文件頁數: | 10/136頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC MICRO KIT GECKO 64QFN |
| 標準包裝: | 1 |
| 系列: | Tiny Gecko |
| 套件類型: | 微控制器 |
| 值: | 2 件 - 閃存 - 32KB |
| 包裝: | 紙板盒 |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 包括封裝: | 64-QFN |
| 工具箱內容: | (2) 914-1035-2-ND - MCU 32BIT 32KB FLASH 64-QFN |
| 其它名稱: | 914-1024 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁當前第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁
...the world's most energy friendly microcontrollers
2011-02-04 - d0002_Rev1.00
107
www.energymicro.com
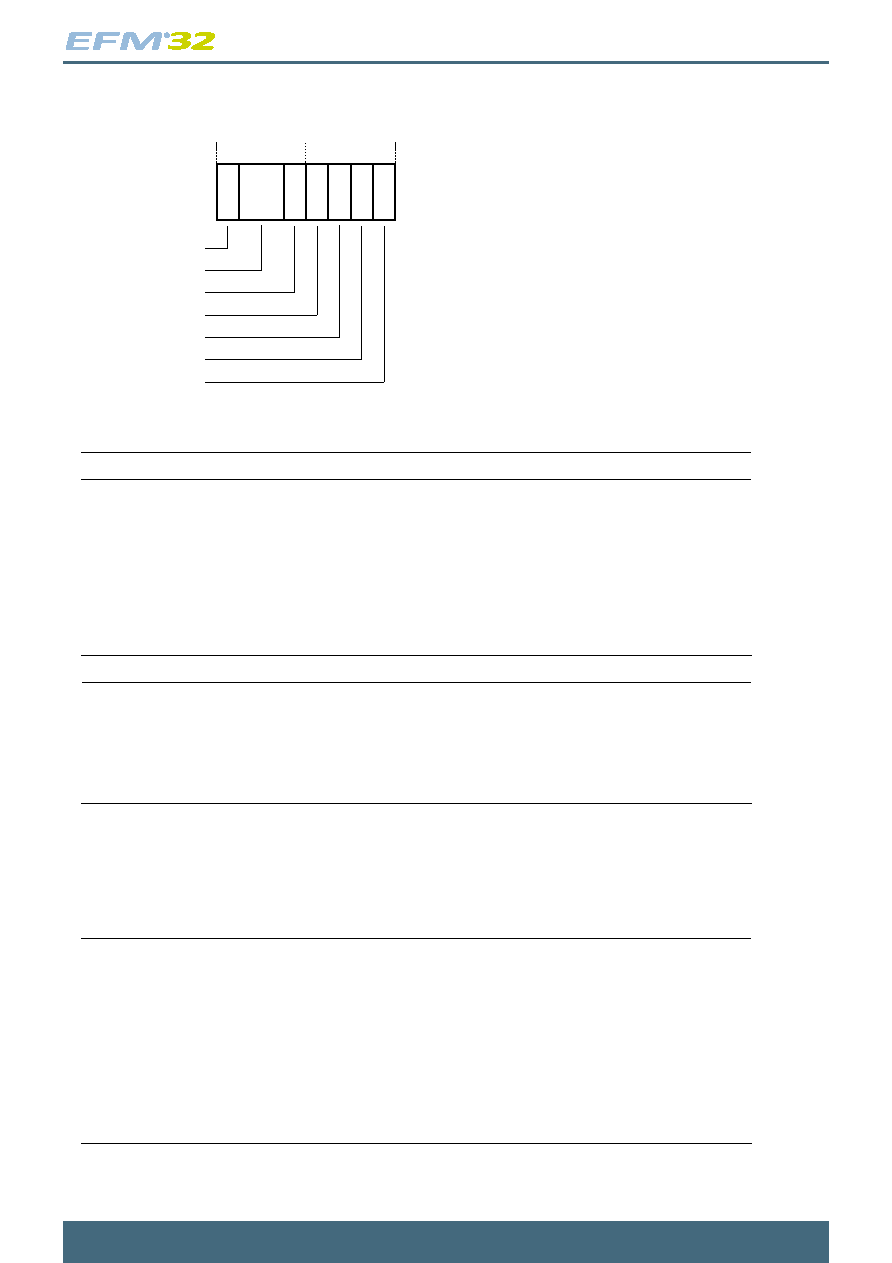
4.3.11.2 Bus Fault Status Register
The flags in the BFSR indicate the cause of a bus access fault. The bit assignments are:
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
BFARVALID
Reserved
STKERR
UNSTKERR
IMPRECISERR
PRECISERR
IBUSERR
Table 4.27. BFSR bit assignments
Bits
Name
Function
[7]
BFARVALID
Bus Fault Address Register (BFAR) valid flag:
0 = value in BFAR is not a valid fault address
1 = BFAR holds a valid fault address.
The processor sets this bit to 1 after a bus fault where the address is known. Other faults can
set this bit to 0, such as a memory management fault occurring later.
If a bus fault occurs and is escalated to a hard fault because of priority, the hard fault handler
must set this bit to 0. This prevents problems if returning to a stacked active bus fault handler
whose BFAR value has been overwritten.
[6:5]
-
Reserved.
[4]
STKERR
Bus fault on stacking for exception entry:
0 = no stacking fault
1 = stacking for an exception entry has caused one or more bus faults.
When the processor sets this bit to 1, the SP is still adjusted but the values in the context area
on the stack might be incorrect. The processor does not write a fault address to the BFAR.
[3]
UNSTKERR
Bus fault on unstacking for a return from exception:
0 = no unstacking fault
1 = unstack for an exception return has caused one or more bus faults.
This fault is chained to the handler. This means that when the processor sets this bit to 1,
the original return stack is still present. The processor does not adjust the SP from the failing
return, does not performed a new save, and does not write a fault address to the BFAR.
[2]
IMPRECISERR
Imprecise data bus error:
0 = no imprecise data bus error
1 = a data bus error has occurred, but the return address in the stack frame is not related to the
instruction that caused the error.
When the processor sets this bit to 1, it does not write a fault address to the BFAR.
This is an asynchronous fault. Therefore, if it is detected when the priority of the current
process is higher than the bus fault priority, the bus fault becomes pending and becomes active
only when the processor returns from all higher priority processes. If a precise fault occurs
before the processor enters the handler for the imprecise bus fault, the handler detects both
IMPRECISERR set to 1 and one of the precise fault status bits set to 1.
[1]
PRECISERR
Precise data bus error:
0 = no precise data bus error
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| EFM32-TG210F32-SK | IC MICRO KIT GECKO 32QFN |
| 1267 X 6" | TAPE ALUMINUM FOIL 6" X 1FT |
| 7810 0.25MM | ECAP COND PAD .25MM 7.7" X 10" |
| 7810 0.20MM | ECAP COND PAD .20MM 7.7" X 10" |
| 1170 X 6" | TAPE FOIL .002" 6" X 18YDS |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| EFM32TG230F32-T | 制造商:Energy Micro AS 功能描述:IC MCU 32BIT 32KB FLASH 64QFN |
| EFM32TG230F8 | 功能描述:ARM微控制器 - MCU 16KB Flash 4KB RAM RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 核心:ARM Cortex M4F 處理器系列:STM32F373xx 數據總線寬度:32 bit 最大時鐘頻率:72 MHz 程序存儲器大小:256 KB 數據 RAM 大小:32 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作電源電壓:1.65 V to 3.6 V, 2 V to 3.6 V, 2.2 V to 3.6 V 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 封裝 / 箱體:LQFP-48 安裝風格:SMD/SMT |
| EFM32TG230F8-QFN64 | 制造商:Energy Micro AS 功能描述:8 FLASH, USART + UART 2, QFN64 - Tape and Reel 制造商:Energy Micro AS 功能描述:IC MCU 32BIT 8KB FLASH 64QFN |
| EFM32TG230F8-QFN64T | 制造商:Energy Micro AS 功能描述:32 BIT ARM MPU, TINY GECKO - Trays |
| EFM32TG230F8-QFN64-T | 制造商:Energy Micro AS 功能描述:IC MCU 32BIT 8KB FLASH 64QFN |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。