- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄98034 > MPSH81RLRE (ON SEMICONDUCTOR) Si, PNP, RF SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | MPSH81RLRE |
| 廠商: | ON SEMICONDUCTOR |
| 元件分類: | 小信號晶體管 |
| 英文描述: | Si, PNP, RF SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, TO-226AA, 3 PIN |
| 文件頁數: | 18/35頁 |
| 文件大小: | 320K |
| 代理商: | MPSH81RLRE |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁當前第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁
Reliability and Quality Assurance
9–12
Motorola Small–Signal Transistors, FETs and Diodes Device Data
OUTGOING QUALITY
The Average Outgoing Quality (AOQ) refers to the number
of devices per million that are outside the specification limits
at the time of shipment. Motorola has established Six Sigma
goals to improve its outgoing quality and will continue its ”error
free performance” focus to achieve its goal of zero parts per
million (PPM) outgoing quality. Motorola’s present quality level
has lead to vendor certification programs with many of its
customers. These programs ensure a level of quality which
allows the customer either to reduce or eliminate the need for
incoming inspections.
AVERAGE OUTGOING QUALITY (AOQ)
CALCULATION
AOQ = (Process Average)
D (Probability of Acceptance)
D (106) (PPM)
D Process Average =
Total Projected Reject Devices
Total Number of Devices
D Projected Reject Devices =
Defects in Sample
Sample Size
D Lot Size
D Total Number of Devices = Sum of units in each submitted lot
D Probability of Acceptance = 1 ±
Number of Lots Rejected
Number of Lots Tested
D 106 = Conversion to parts per million (PPM)
RELIABILITY DATA ANALYSIS
Reliability is the probability that a semiconductor device will
perform its specified function in a given environment for a
specified period. In other words, reliability is quality over time
and environmental conditions. The most frequently used
reliability measure for semiconductor devices is the failure
rate (
λ ). The failure rate is obtained by dividing the number
of failures observed by the product of the number of devices
on test and the interval in hours, usually expressed as percent
per thousand hours or failures per billion device hours (FITS).
This is called a point estimate because it is obtained from
observations on a portion (sample) of the population of
devices.
To project from the sample to the population in general, one
must establish confidence intervals. The application of
confidence intervals is a statement of how ‘‘confident’’ one is
that the sample failure rate approximates that for the
population. To obtain failure rates at different confidence
levels, it is necessary to make use of specific probability
distributions. The chi–square (
χ2) distribution that relates
observed and expected frequencies of an event is frequently
used to establish confidence intervals. The relationship
between failure rate and the chi–square distribution is as
follows:
λ =
χ2 (α, d. f.)
2t
where:
λ = failure rate
χ2 = chi–square function
α = (100 – confidence level) / 100
d.f. = degrees of freedom = 2r + 2
r = number of failures
t = device hours
Chi–square values for 60% and 90% confidence intervals for
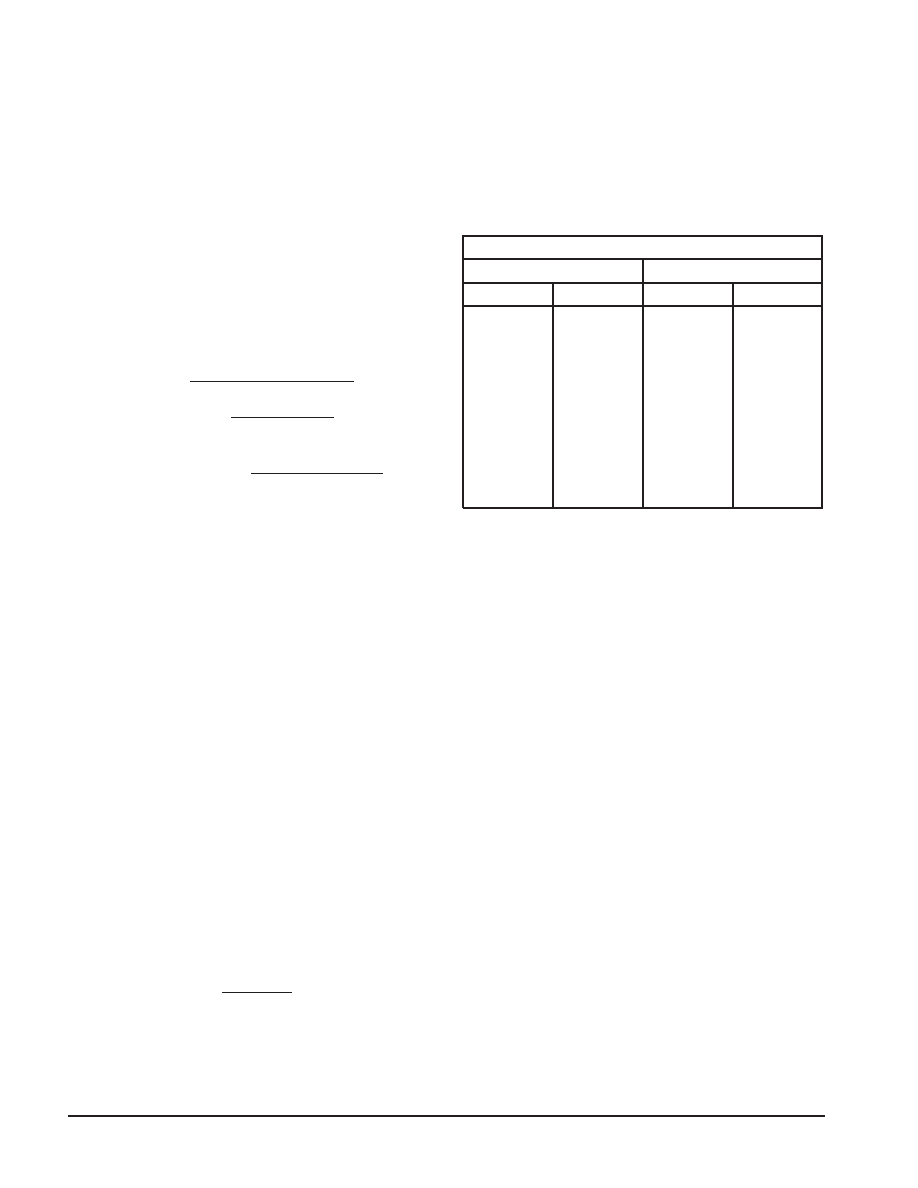
up to 12 failures are shown in Table 1–1.
Table 1–1 – Chi–Square Table
Chi–Square Distribution Function
60% Confidence Level
90% Confidence Level
No. Fails
χ2 Quantity
No. Fails
χ2 Quantity
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1.833
4.045
6.211
8.351
10.473
12.584
14.685
16.780
18.868
20.951
23.031
25.106
27.179
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
4.605
7.779
10.645
13.362
15.987
18.549
21.064
23.542
25.989
28.412
30.813
33.196
35.563
The failure rate of semiconductor devices is inherently low.
As a result, the industry uses a technique called accelerated
testing to assess the reliability of semiconductors. During
accelerated tests, elevated stresses are used to produce, in
a short period, the same failure mechanisms as would be
observed under normal use conditions. The objective of this
testing is to identify these failure mechanisms and eliminate
them as a cause of failure during the useful life of the product.
Temperature, relative humidity, and voltage are the most
frequently used stresses during accelerated testing. Their
relationship to failure rates has been shown to follow an Eyring
type of equation of the form:
λ = A exp(φkT) exp(B/RH) exp(CE)
Where A, B, C,
φ, and k are constants, more specifically B,
C, and
φ are numbers representing the apparent energy at
which various failure mechanisms occur. These are called
activation energies. ‘‘T’’ is the temperature, ‘‘RH’’ is the
relative humidity, and ‘‘E’’ is the electric field. The most familiar
form of this equation (shown on following page) deals with the
first exponential term that shows an Arrhenius type
relationship of the failure rate versus the junction temperature
of semiconductors. The junction temperature is related to the
ambient temperature through the thermal resistance and
power dissipation. Thus, we can test devices near their
maximum junction temperatures, analyze the failures to
assure that they are the types that are accelerated by
temperature and then by applying known acceleration factors,
estimate the failure rates for lower junction.
The table on the following page shows observed activation
energies with references.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MPSH81 | Si, PNP, RF SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| MPSL01ZL1 | 150 mA, 120 V, NPN, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| MPSL01RLRA | 150 mA, 120 V, NPN, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| MPSL01RL1 | 150 mA, 120 V, NPN, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
| MPSL01RLRM | 150 mA, 120 V, NPN, Si, SMALL SIGNAL TRANSISTOR, TO-92 |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| MPSH8-D20-120V | 制造商:Black Box Corporation 功能描述:8 OUTLET 120V 20A DUAL CIRCUIT OUTLET METERING |
| MPSH8-D20-120V-W1 | 制造商:Black Box Corporation 功能描述:1 YEAR WARRANTY FOR MPSH8-D20-120V |
| MPSH8-D20-120V-W3 | 制造商:Black Box Corporation 功能描述:3 YEAR WARRANTY FOR MPSH8-D20-120V |
| MPSH8-D20-208+V | 制造商:Black Box Corporation 功能描述:8 OUTLET 208+V 20A DUAL CIRCUIT OUTLET METERING |
| MPSH8-D20-208+VT | 制造商:Black Box Corporation 功能描述:8 OUTLET 208+V 20A DUAL CIRCUIT OUTLET METERING |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。