- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373916 > AD7755AAN-REF (Analog Devices, Inc.) GT 7C 7#8 SKT RECP PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | AD7755AAN-REF |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | GT 7C 7#8 SKT RECP |
| 中文描述: | 電能計量IC輸出脈沖 |
| 文件頁數: | 10/16頁 |
| 文件大小: | 250K |
| 代理商: | AD7755AAN-REF |
REV. B
AD7755
–10–
THEORY OF OPERATION
The two ADCs digitize the voltage signals from the current and
voltage transducers. These ADCs are 16-bit second order
sigma-delta with an oversampling rate of 900 kHz. This analog
input structure greatly simplifies transducer interfacing by
providing a wide dynamic range for direct connection to the
transducer and also simplifying the antialiasing filter design. A
programmable gain stage in the current channel further facili-
tates easy transducer interfacing. A high pass filter in the current
channel removes any dc component from the current signal.
This eliminates any inaccuracies in the real power calculation
due to offsets in the voltage or current signals—see HPF and
Offset Effects section.
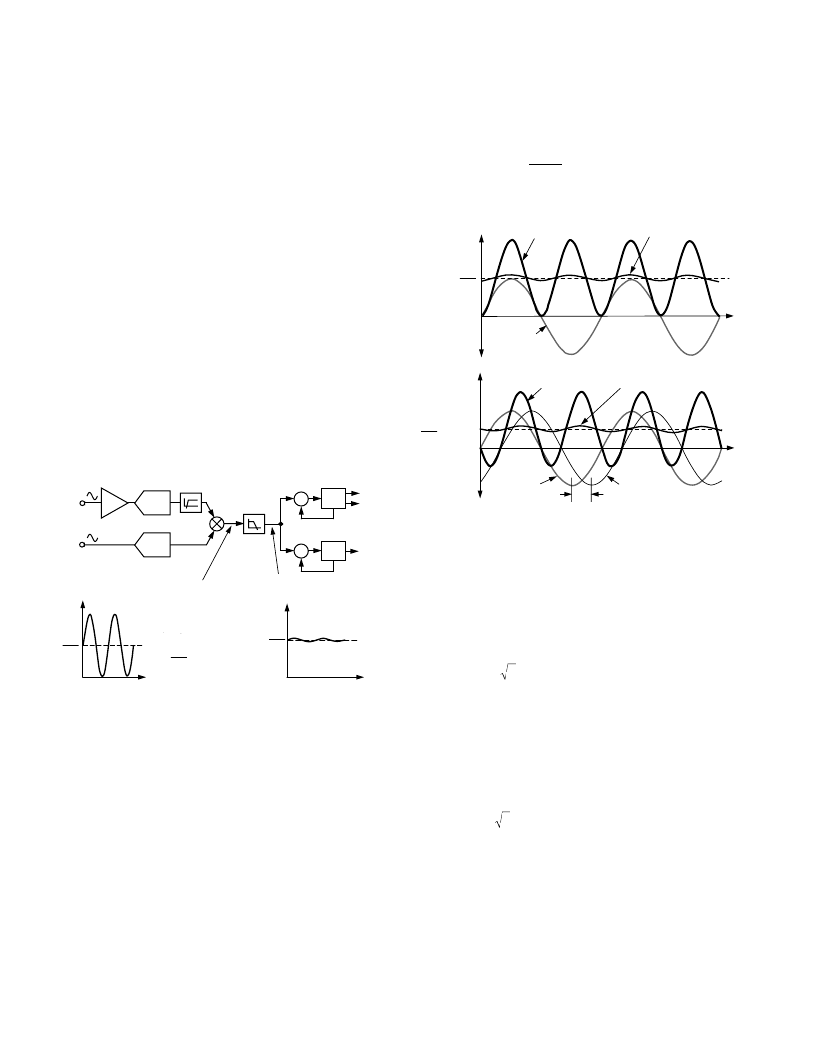
The real power calculation is derived from the instantaneous
power signal. The instantaneous power signal is generated by a
direct multiplication of the current and voltage signals. In order
to extract the real power component (i.e., the dc component),
the instantaneous power signal is low-pass filtered. Figure 20
illustrates the instantaneous real power signal and shows how the
real power information can be extracted by low-pass filtering the
instantaneous power signal. This scheme correctly calculates real
power for nonsinusoidal current and voltage waveforms at all
power factors. All signal processing is carried out in the digital
domain for superior stability over temperature and time.
LPF
DIGITAL-TO-
FREQUENCY
F1
F2
CH1
INSTANTANEOUS REAL
POWER SIGNAL
MULTIPLIER
PGA
CH2
ADC
INSTANTANEOUS
POWER SIGNAL
–
p(t)
V
I
2
V
I
V I
2
p(t) = i(t)
WHERE:
v(t) = V
i(t) = I
p(t) =V
v(t)
cos( t)
cos( t)
I
2
{
1+cos (2 t)}
ADC
TIME
HPF
DIGITAL-TO-
FREQUENCY
CF
Figure 20. Signal Processing Block Diagram
The low frequency output of the AD7755 is generated by accu-
mulating this real power information. This low frequency inher-
ently means a long accumulation time between output pulses.
The output frequency is therefore proportional to the average
real power. This average real power information can, in turn, be
accumulated (e.g., by a counter) to generate real energy infor-
mation. Because of its high output frequency and hence shorter
integration time, the CF output is proportional to the instanta-
neous real power. This is useful for system calibration purposes
that would take place under steady load conditions.
Power Factor Considerations
The method used to extract the real power information from the
instantaneous power signal (i.e., by low-pass filtering) is still
valid even when the voltage and current signals are not in phase.
Figure 21 displays the unity power factor condition and a DPF
(Displacement Power Factor) = 0.5, i.e., current signal lagging
the voltage by 60
°
. If we assume the voltage and current wave-
forms are sinusoidal, the real power component of the instanta-
neous power signal (i.e., the dc term) is given by
2
This is the correct real power calculation.
V
I
×
×
cos (60
°
).
INSTANTANEOUS
REAL POWER SIGNAL
INSTANTANEOUS
POWER SIGNAL
V I
2
cos(60 )
V I
2
INSTANTANEOUS
POWER SIGNAL
INSTANTANEOUS
REAL POWER SIGNAL
60
CURRENT
CURRENT
VOLTAGE
0V
0V
VOLTAGE
Figure 21. DC Component of Instantaneous Power Signal
Conveys Real Power Information PF < 1
Nonsinusoidal Voltage and Current
The real power calculation method also holds true for nonsinu-
soidal current and voltage waveforms. All voltage and current
waveforms in practical applications will have some harmonic
content. Using the Fourier Transform, instantaneous voltage
and current waveforms can be expressed in terms of their har-
monic content.
∞
∑
0
v t
( )
V
Vh
h t
h
O
h
sin(
)
=
+
×
×
+
≠
2
α
(1)
where:
v
(
t
)
V
O
Vh
and
h
is the instantaneous voltage
is the average value
is the rms value of voltage harmonic
h
is the phase angle of the voltage harmonic.
∞
∑
0
i t
( )
I
Ih
h t
h
O
h
sin(
)
=
+
×
×
+
≠
2
β
(2)
where:
i
(
t
)
I
O
Ih
and
h
is the instantaneous current
is the dc component
is the rms value of current harmonic
h
is the phase angle of the current harmonic.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7755AARS | Energy Metering IC with Pulse Output |
| AD7755ABRS | Energy Metering IC with Pulse Output |
| AD7755AAN | Energy Metering IC with Pulse Output |
| AD7760 | 2.5 MSPS, 20-Bit ADC |
| AD7760BCP | 2.5 MSPS, 20-Bit ADC |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7755AARS | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:ENERGY METERING IC WITH P - Bulk 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述: |
| ad7755aarsrl | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:ENERGY METERING IC WITH P - Tape and Reel 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述: |
| AD7755ABRS | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:Energy Metering IC with Pulse Output |
| AD7755AN | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:ENERGY METERING IC WITH P - Bulk |
| AD7755ARS | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。