- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373911 > AD7654AST (ANALOG DEVICES INC) Dual 2-Channel Simultaneous Sampling SAR 500 kSPS 16-Bit ADC PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | AD7654AST |
| 廠商: | ANALOG DEVICES INC |
| 元件分類: | ADC |
| 英文描述: | Dual 2-Channel Simultaneous Sampling SAR 500 kSPS 16-Bit ADC |
| 中文描述: | 4-CH 16-BIT SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC, SERIAL/PARALLEL ACCESS, PQFP48 |
| 封裝: | MS-026-BBC, LQFP-48 |
| 文件頁數: | 17/24頁 |
| 文件大小: | 734K |
| 代理商: | AD7654AST |
REV. 0
AD7654
–17–
mode, channel A data is updated only after channel B conver-
sion. This data is synchronized with the 32 clock pulses provided
on the SCLK pin.
MASTER SERIAL INTERFACE
Internal Clock
The AD7654 is configured to generate and provide the serial
data clock SCLK when the EXT/
INT
pin is held low. The
AD7654 also generates a SYNC signal to indicate to the host
when the serial data is valid. The serial clock SCLK and the
SYNC signal can be inverted if desired. The output data is valid
on both the rising and falling edge of the data clock. Depending
on RDC/SDIN input, the data can be read after each conver-
sion or during the following conversion.
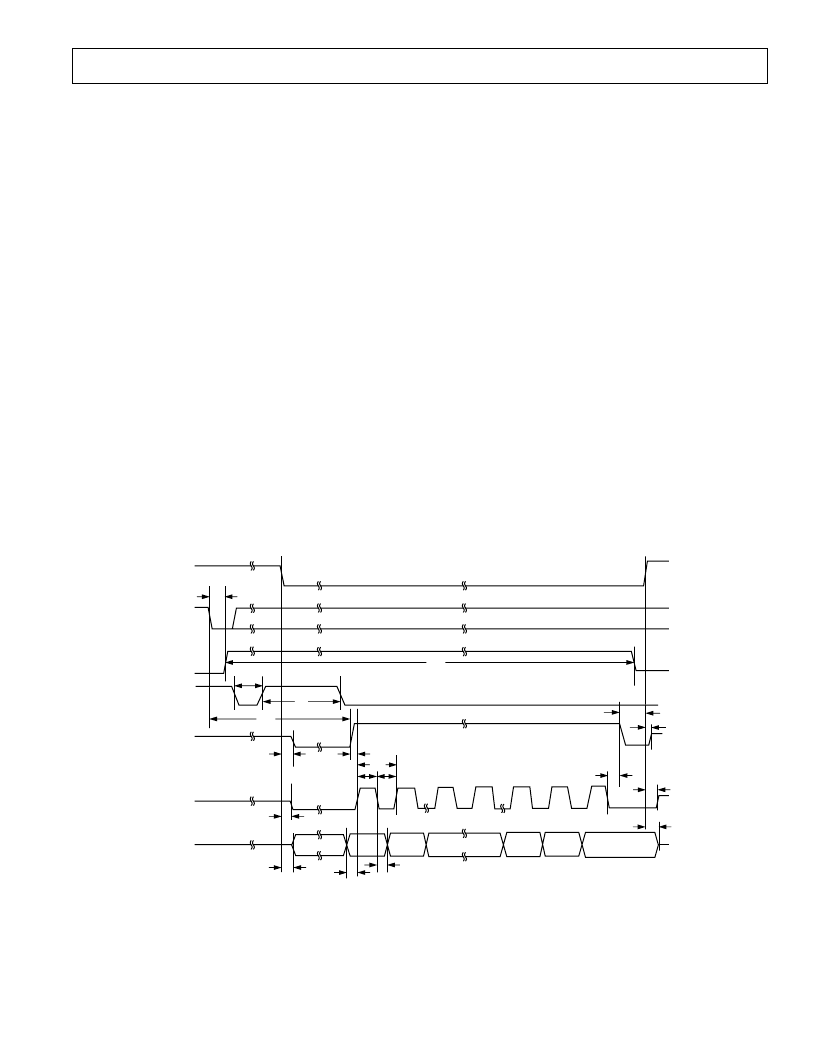
Figures 15 and 16 show the detailed timing diagrams of these
two modes.
Usually, because the AD7654 is used with a fast throughput,
the mode Master Read during Conversion is the most recom-
mended serial mode when it can be used.
In Read-after-Conversion Mode, it should be noted that unlike
in other modes, the signal BUSY returns low after the 32 data
bits are pulsed out and not at the end of the conversion phase,
which results in a longer BUSY width. One advantage of this
mode is that it can accommodate slow digital hosts because the
serial clock can be slowed down by using DIVSCLK.
In Read-during-Conversion Mode, the serial clock and data toggle
at appropriate instants, which minimizes potential feedthrough
between digital activity and the critical conversion decisions.
The SYNC signal goes low after the LSB of each channel has
been output.
SLAVE SERIAL INTERFACE
External Clock
The AD7654 is configured to accept an externally supplied serial
data clock on the SCLK pin when the EXT/
INT
pin is held
high. In this mode, several methods can be used to read the
data. The external serial clock is gated by
CS
and the data are
output when both
CS
and
RD
are low. Thus, depending on
CS
,
the data can be read after each conversion or during the follow-
ing conversion. The external clock can be either a continuous or
discontinuous clock. A discontinuous clock can be either normally
high or normally low when inactive. Figures 17 and 18 show the
detailed timing diagrams of these methods.
While the AD7654 is performing a bit decision, it is important
that voltage transients not occur on digital input/output pins or
degradation of the conversion result could occur. This is par-
ticularly important during the second half of the conversion
phase of each channel because the AD7654 provides error cor-
rection circuitry that can correct for an improper bit decision
made during the first half of the conversion phase. For this
reason, it is recommended that when an external clock is pro-
vided, it is a discontinuous clock that is toggling only when
BUSY is low or, more importantly, that it does not transition
during the latter half of EOC high.
t
3
BUSY
CS
,
RD
CNVST
SYNC
SCLK
SDOUT
1
2
16
30
31
32
CH A
D15
CH A
D14
t
30
CH B
D2
CH B
D1
CH B D0
X
EXT/
INT
= 0
RDC/SDIN = 0
INVSCLK = INVSYNC = 0
t
21
t
27
t
22
t
23
t
29
t
36
t
25
t
26
t
28
t
37
t
32
t
31
t
33
t
34
A/
B
= 1
EOC
t
12
t
13
17
t
35
Figure 15. Master Serial Data Timing for Reading (Read after Convert)
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7654ASTRL | Dual 2-Channel Simultaneous Sampling SAR 500 kSPS 16-Bit ADC |
| AD7655 | Low Cost 4-Channel 1 MSPS 16-Bit ADC |
| AD7655ACP | Low Cost 4-Channel 1 MSPS 16-Bit ADC |
| AD7655ACPRL | Low Cost 4-Channel 1 MSPS 16-Bit ADC |
| AD7655AST | Low Cost 4-Channel 1 MSPS 16-Bit ADC |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7654ASTRL | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:ADC Single SAR 500ksps 16-bit Parallel/Serial 48-Pin LQFP T/R |
| AD7654ASTZ | 功能描述:IC ADC 16BIT 500KSPS DUAL 48LQFP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 數據采集 - 模數轉換器 系列:PulSAR® 標準包裝:1 系列:microPOWER™ 位數:8 采樣率(每秒):1M 數據接口:串行,SPI? 轉換器數目:1 功率耗散(最大):- 電壓電源:模擬和數字 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 125°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:24-VFQFN 裸露焊盤 供應商設備封裝:24-VQFN 裸露焊盤(4x4) 包裝:Digi-Reel® 輸入數目和類型:8 個單端,單極 產品目錄頁面:892 (CN2011-ZH PDF) 其它名稱:296-25851-6 |
| AD7654ASTZ | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:IC 16BIT ADC SMD 7654 LQFP48 |
| AD7654ASTZRL | 功能描述:IC ADC 16BIT DUAL 2CH 48LQFP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 數據采集 - 模數轉換器 系列:PulSAR® 標準包裝:1,000 系列:- 位數:12 采樣率(每秒):300k 數據接口:并聯 轉換器數目:1 功率耗散(最大):75mW 電壓電源:單電源 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:24-SOIC(0.295",7.50mm 寬) 供應商設備封裝:24-SOIC 包裝:帶卷 (TR) 輸入數目和類型:1 個單端,單極;1 個單端,雙極 |
| AD7655 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:14-Bit, 1 MSPS, Differential, Programmable Input PulSAR ADC |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。