- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373916 > AD7760BSV (ANALOG DEVICES INC) 2.5 MSPS, 20-Bit ADC PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | AD7760BSV |
| 廠商: | ANALOG DEVICES INC |
| 元件分類: | ADC |
| 英文描述: | 2.5 MSPS, 20-Bit ADC |
| 中文描述: | 1-CH 20-BIT DELTA-SIGMA ADC, PARALLEL ACCESS, PQFP64 |
| 封裝: | TQFP-64 |
| 文件頁數: | 10/22頁 |
| 文件大小: | 868K |
| 代理商: | AD7760BSV |
AD7760
Preliminary Technical Data
TERMINOLOGY
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) Ratio
The measured ratio of signal to (noise + distortion) at the
output of the ADC. The signal is the rms amplitude of the
fundamental. Noise is the sum of all nonfundamental signals up
to half the sampling frequency (f
S
/2), excluding dc. The ratio is
dependent on the number of quantization levels in the
digitization process; the more levels, the smaller the
quantization noise. The theoretical signal to (noise + distortion)
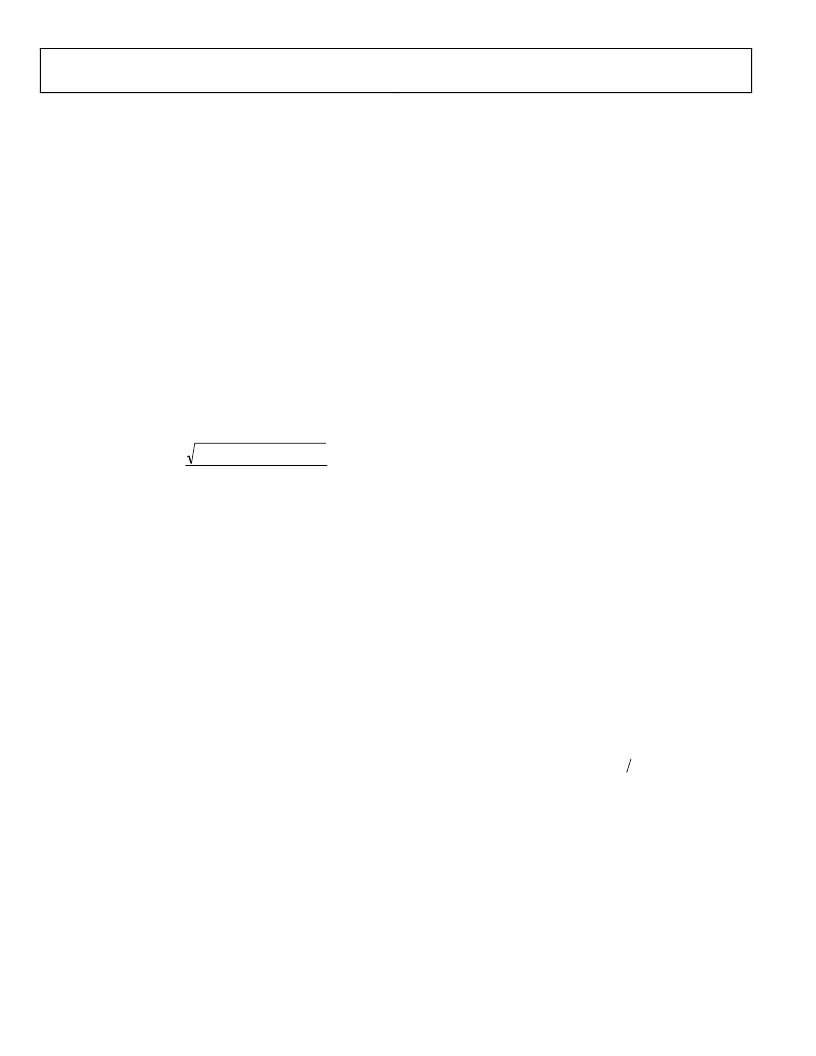
ratio for an ideal N-bit converter with a sine wave input is given
by
(
Distortion
Noise
to
Signal
+
Rev. PrN | Page 10 of 22
)
(
.
)
dB
N
76
.
02
+
=
Thus, for an 18-bit converter, this is 110.12dBs and for a 20-bit
converter, 122.16 dB.
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
The ratio of the rms sum of harmonics to the fundamental. For
the AD7760, it is defined as
(
)
1
2
6
2
5
2
4
2
3
2
2
V
V
V
V
V
V
20
dB
THD
+
+
+
+
=
log
where:
V
1
is the rms amplitude of the fundamental.
V
2
, V
3
, V
4
, V
5
, and V
6
are the rms amplitudes of the second to the
sixth harmonics.
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise
The ratio of the rms value of the next largest component in the
ADC output spectrum (up to f
S
/2 and excluding dc) to the rms
value of the fundamental. Normally, the value of this
specification is determined by the largest harmonic in the
spectrum, but, for ADCs where the harmonics are buried in the
noise floor, it is a noise peak.
Non-Harmonic Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the
peak spurious spectral component excluding harmonics.
Intermodulation Distortion
With inputs consisting of sine waves at two frequencies, fa and
fb, any active device with nonlinearities creates distortion
products at sum and difference frequencies of mfa ± nfb, where
m, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. Intermodulation distortion terms are
those for which neither m nor n are equal to zero. For example,
the second-order terms include (fa + fb) and (fa fb), while the
third-order terms include (2fa + fb), (2fa fb), (fa + 2fb) and (fa
2fb).
The AD7760 is tested using the CCIF standard, where two input
frequencies near the top end of the input bandwidth are used.
In this case, the second-order terms are usually distanced in
frequency from the original sine waves, while the third-order
terms are usually at a frequency close to the input frequencies.
As a result, the second- and third-order terms are specified
separately. The calculation of the intermodulation distortion is
as per the THD specification, where it is the ratio of the rms
sum of the individual distortion products to the rms amplitude
of the sum of the fundamentals expressed in dB.
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
The maximum deviation from a straight line passing through
the endpoints of the ADC transfer function.
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
The difference between the measured and the ideal 1 LSB
change between any two adjacent codes in the ADC.
Offset Error
The deviation of the first code transition (000...000 to 000...001)
from the ideal (that is, AGND + 1 LSB).
Gain Error
The deviation of the last code transition (111...110 to 111...111)
from the ideal (that is, V
REF
1 LSB), after the offset error has
been adjusted out.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
The ratio of the power in the ADC output at full-scale
frequency, f, to the power of a 100 mV p-p sine wave applied to
the ADC V
DD
supply of frequency fs. The frequency of this
input varies from 1 kHz to 1 MHz.
(
)
dB
PSRR
10
=
(
)
Pfs
Pf
log
P
f
is the power at frequency f in the ADC output; P
f
s is the
power at frequency fs in the ADC output.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7769 | LC2MOS Analog I/O Port |
| AD7769AN | LC2MOS Analog I/O Port |
| AD7769AP | LC2MOS Analog I/O Port |
| AD7769JN | LC2MOS Analog I/O Port |
| AD7769JP | LC2MOS Analog I/O Port |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7760BSVZ | 功能描述:IC ADC 24BIT 2.5MSPS 64TQFP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 數據采集 - 模數轉換器 系列:- 其它有關文件:TSA1204 View All Specifications 標準包裝:1 系列:- 位數:12 采樣率(每秒):20M 數據接口:并聯 轉換器數目:2 功率耗散(最大):155mW 電壓電源:模擬和數字 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:48-TQFP 供應商設備封裝:48-TQFP(7x7) 包裝:Digi-Reel® 輸入數目和類型:4 個單端,單極;2 個差分,單極 產品目錄頁面:1156 (CN2011-ZH PDF) 其它名稱:497-5435-6 |
| AD7760BSVZ-REEL | 功能描述:IC ADC 24BIT 2.5MSPS 64TQFP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 數據采集 - 模數轉換器 系列:- 標準包裝:1 系列:- 位數:14 采樣率(每秒):83k 數據接口:串行,并聯 轉換器數目:1 功率耗散(最大):95mW 電壓電源:雙 ± 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 安裝類型:通孔 封裝/外殼:28-DIP(0.600",15.24mm) 供應商設備封裝:28-PDIP 包裝:管件 輸入數目和類型:1 個單端,雙極 |
| AD7761BSTZ | 功能描述:16 Bit Analog to Digital Converter 8 Input 8 Sigma-Delta 64-LQFP (10x10) 制造商:analog devices inc. 系列:- 包裝:托盤 零件狀態:有效 位數:16 采樣率(每秒):256k 輸入數:8 輸入類型:差分 數據接口:SPI 配置:ADC 無線電 - S/H:ADC:- A/D 轉換器數:8 架構:三角積分 參考類型:外部 電壓 - 電源,模擬:2 V ~ 5.5 V 電壓 - 電源,數字:- 特性:同步采樣 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 105°C 封裝/外殼:64-LQFP 供應商器件封裝:64-LQFP(10x10) 標準包裝:1 |
| AD7761BSTZ-RL | 功能描述:16 Bit Analog to Digital Converter 8 Input 8 Sigma-Delta 64-LQFP (10x10) 制造商:analog devices inc. 系列:- 包裝:帶卷(TR) 零件狀態:有效 位數:16 采樣率(每秒):256k 輸入數:8 輸入類型:差分 數據接口:SPI 配置:ADC 無線電 - S/H:ADC:- A/D 轉換器數:8 架構:三角積分 參考類型:外部 電壓 - 電源,模擬:2 V ~ 5.5 V 電壓 - 電源,數字:- 特性:同步采樣 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 105°C 封裝/外殼:64-LQFP 供應商器件封裝:64-LQFP(10x10) 標準包裝:1,500 |
| AD7762 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:24-Bit, 8.5 mW, 109 dB, 128/64/32 kSPS ADCs |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。