- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373983 > ADF7020 (Analog Devices, Inc.) High Performance ISM Band FSK/ASK Transceiver IC PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | ADF7020 |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | High Performance ISM Band FSK/ASK Transceiver IC |
| 中文描述: | 高性能ISM頻段FSK信號/賣出收發芯片 |
| 文件頁數: | 24/40頁 |
| 文件大小: | 797K |
| 代理商: | ADF7020 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁當前第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁
ADF7020
Preliminary Technical Data
SERIAL INTERFACE
The serial interface allows the user to program the eleven 32-bit
registers using a 3-wire interface (SCLK, SDATA, and SLE). It
consists of a level shifter, 32-bit shift register and eleven latches.
Signals should be CMOS compatible. The serial interface is
powered by the regulator, and, therefore, is inactive when CE is
low.
Rev. PrH | Page 24 of 40
Data is clocked into the register, MSB first, on the rising edge of
each clock (SCLK). Data is transferred to one of eleven latches
on the rising edge of SLE. The destination latch is determined
by the value of the four control bits (C4 to C1). These are the
bottom four LSBs, DB3 to DB0, as shown in the timing diagram
in Figure 2. Data can also be read back on the SREAD pin.
READBACK FORMAT
The readback operation is initiated by writing a valid control
word to the readback register and setting the readback-enable
bit (R7_DB8 = 1). The readback can begin after the control
word has been latched with the SLE signal. SLE must be kept
high while the data is being read out. Each active edge at the
SCLK pin clocks the readback word out successively at the
SREAD pin, as shown in Figure 25, starting with the MSB first.
The data appearing at the first clock cycle following the latch
operation must be ignored.
AFC Readback
The AFC readback is valid only during the reception of FSK
signals with either the linear or correlator demodulator active.
The AFC readback value is formatted as a signed 16-bit integer
comprised of Bits RV1 to RV16, and is scaled according to the
following formula:
FREQ_RB
[Hz] = (
AFC_READBACK
×
DEMOD_CLK
)/2
15
In the absence of frequency errors, the FREQ_RB value is equal
to the IF frequency of 200 kHz. Note that, for the AFC readback
to yield a valid result, the down-converted input signal must not
fall outside the bandwidth of the analogue IF filter. At low-input
signal levels, the variation in the readback value can be
improved by averaging.
RSSI Readback
The RSSI readback operation yields valid results in Rx mode
with ASK or FSK signals. The format of the readback word is
shown in Figure 25. It is comprised of the RSSI level informa-
tion (Bits RV1 to RV7), the current filter gain (FG1, FG2), and
the current LNA gain (LG1, LG2) setting. The filter and LNA
gain are coded in accordance with the definitions in Register 9.
With the reception of ASK modulated signals, averaging of the
measured RSSI values improves accuracy. The input power can
be calculated from the RSSI readback value as outlined in the
RSSI/AGC Section.
Battery Voltage ADCIN/Temperature Sensor Readback
The battery voltage is measured at Pin VDD4. The readback
information is contained in Bits RV1 to RV7. This also applies
for the readback of the voltage at the ADCIN pin and the
temperature sensor. From the readback information, the battery
or ADCIN voltage can be determined using
V
BATTERY
= (
Battery_Voltage_Readback
)/21.1
V
ADCIN
= (
ADCIN_Voltage_Readback
)/42.1
Silicon Revision Readback
The silicon revision readback word is valid without setting any
other registers, especially directly after power-up. The silicon
revision word is coded with four quartets in BCD format. The
product code (PC) is coded with two quartets extending from
Bits RV9 to RV16. The revision code (RV) is coded with two
quartets extending from Bits RV1 to RV8. The product code
should read back as PC = #20h. The current revision code
should read as RC = #30h.
Filter Calibration Readback
The filter calibration readback word is contained in Bits RV1 to
RV8, and is for diagnostic purposes only. Using the automatic
filter calibration function, accessible through Register 6, is
recommended.
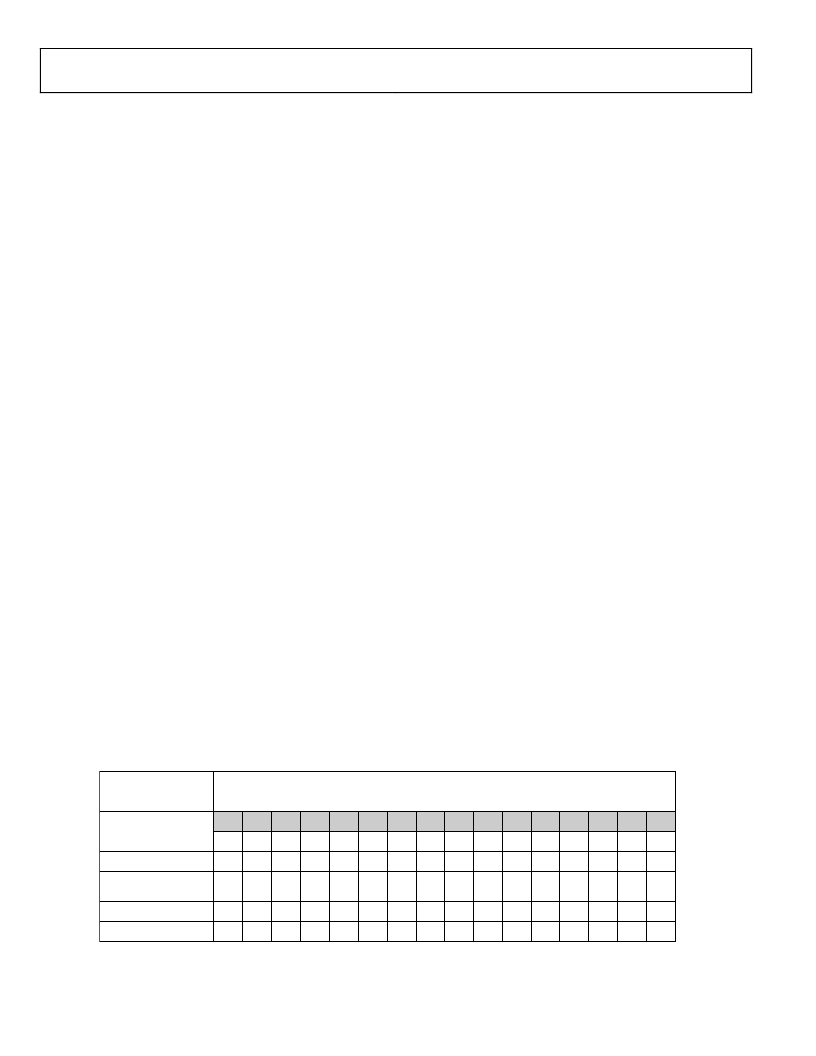
0
READBACK MODE
AFC READBACK
DB15
RV16
X
X
RV16
0
RSSI READBACK
BATTERY VOLTAGE/ADCIN/
TEMP. SENSOR READBACK
SILICON REVISION
FILTER CAL READBACK
READBACK VALUE
DB14
RV15
X
X
RV15
0
DB13
RV14
X
X
RV14
0
DB12
RV13
X
X
RV13
0
DB11
RV12
X
X
RV12
0
DB10
RV11
LG2
X
RV11
0
DB9
RV10
LG1
X
RV10
0
DB8
RV9
FG2
X
RV9
0
DB7
RV8
FG1
X
RV8
RV8
DB6
RV7
RV7
RV7
RV7
RV7
DB5
RV6
RV6
RV6
RV6
RV6
DB4
RV5
RV5
RV5
RV5
RV5
DB3
RV4
RV4
RV4
RV4
RV4
DB2
RV3
RV3
RV3
RV3
RV3
DB1
RV2
RV2
RV2
RV2
RV2
DB0
RV1
RV1
RV1
RV1
RV1
Figure 25. Readback Value Table
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ADF7020BCP | High Performance ISM Band FSK/ASK Transceiver IC |
| ADG1204 | 2 pF Off Capacitance, 1 pC Charge Injection, +-15 V/12 V 4:1 iCMOS Multiplexer |
| ADG1204YCP | 2 pF Off Capacitance, 1 pC Charge Injection, +-15 V/12 V 4:1 iCMOS Multiplexer |
| ADG1204YRU | 2 pF Off Capacitance, 1 pC Charge Injection, +-15 V/12 V 4:1 iCMOS Multiplexer |
| ADG202A | Quad SPST Switches(LC2MOS四單刀單擲開關) |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| ADF7020-1 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:High Performance FSK/ASK Transceiver IC |
| ADF7020-1BCPZ | 功能描述:IC TX FSK/ASK ISM BAND 48LFCSP RoHS:是 類別:RF/IF 和 RFID >> RF 收發器 系列:- 產品培訓模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標準包裝:30 系列:- 頻率:4.9GHz ~ 5.9GHz 數據傳輸率 - 最大:54Mbps 調制或協議:* 應用:* 功率 - 輸出:-3dBm 靈敏度:- 電源電壓:2.7 V ~ 3.6 V 電流 - 接收:* 電流 - 傳輸:* 數據接口:PCB,表面貼裝 存儲容量:- 天線連接器:PCB,表面貼裝 工作溫度:-25°C ~ 85°C 封裝/外殼:68-TQFN 裸露焊盤 包裝:管件 |
| ADF7020-1BCPZ-RL | 功能描述:IC TX FSK/ASK ISM BAND 48-LFCSP RoHS:是 類別:RF/IF 和 RFID >> RF 收發器 系列:- 產品培訓模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標準包裝:30 系列:- 頻率:4.9GHz ~ 5.9GHz 數據傳輸率 - 最大:54Mbps 調制或協議:* 應用:* 功率 - 輸出:-3dBm 靈敏度:- 電源電壓:2.7 V ~ 3.6 V 電流 - 接收:* 電流 - 傳輸:* 數據接口:PCB,表面貼裝 存儲容量:- 天線連接器:PCB,表面貼裝 工作溫度:-25°C ~ 85°C 封裝/外殼:68-TQFN 裸露焊盤 包裝:管件 |
| ADF7020-1BCPZ-RL7 | 功能描述:IC TX FSK/ASK ISM BAND 48-LFCSP RoHS:是 類別:RF/IF 和 RFID >> RF 收發器 系列:- 產品培訓模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標準包裝:30 系列:- 頻率:4.9GHz ~ 5.9GHz 數據傳輸率 - 最大:54Mbps 調制或協議:* 應用:* 功率 - 輸出:-3dBm 靈敏度:- 電源電壓:2.7 V ~ 3.6 V 電流 - 接收:* 電流 - 傳輸:* 數據接口:PCB,表面貼裝 存儲容量:- 天線連接器:PCB,表面貼裝 工作溫度:-25°C ~ 85°C 封裝/外殼:68-TQFN 裸露焊盤 包裝:管件 |
| ADF7020BCP | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:High Performance ISM Band FSK/ASK Transceiver IC |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。