- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄365968 > TSB14AA1 FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | TSB14AA1 |
| 英文描述: | FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) |
| 中文描述: | 電機(jī)及電子學(xué)工程師聯(lián)合會(huì)1394-1995。 3.3。 1-port.50/100Mbps。底板PHY |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 24/35頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 224K |
| 代理商: | TSB14AA1 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)當(dāng)前第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)
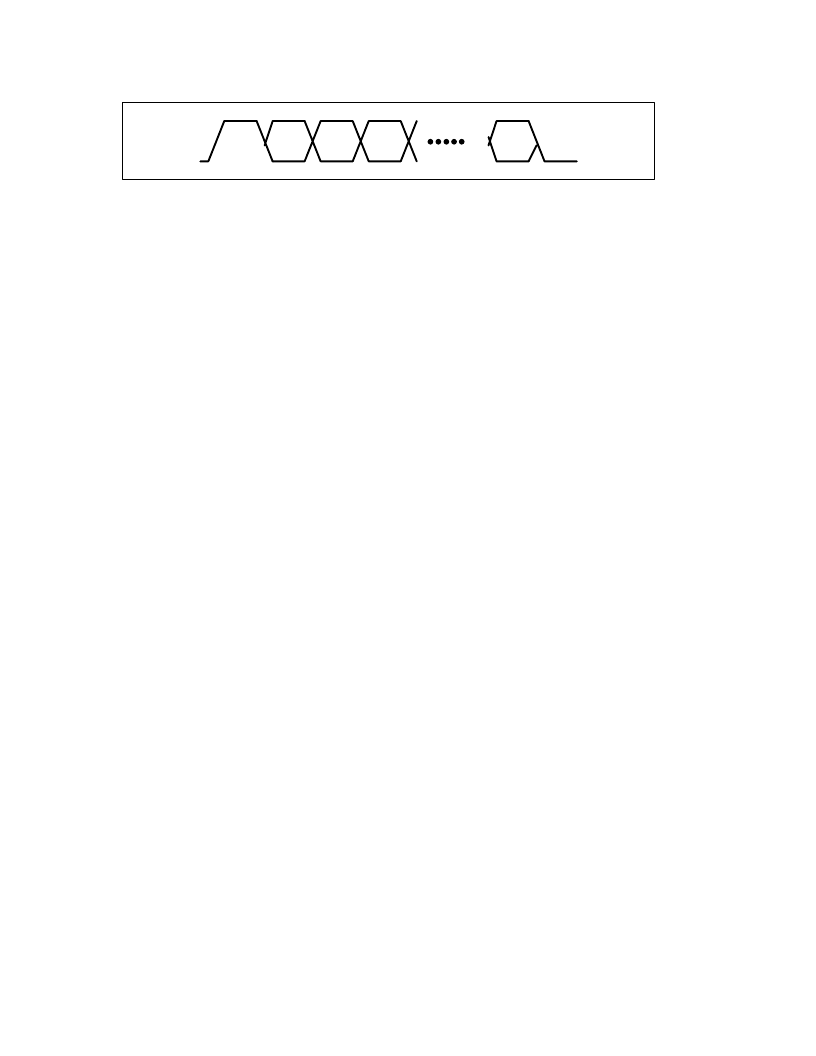
6
–
4
LReq0
LReq1
LReq2
LReqN
LReq3
Figure 6
–
2. LREQ Timing
6.1.1
Bus Request
For fair or priority access, the link requests control of the bus at least one clock cycle after the PHY
–
link interface
becomes idle. When the link senses that the CTL terminals are in a receive state (CTL0 and CTL1 = 10), then it knows
that its request has been lost. This is true anytime during or after a bus request transfer by the link. Additionally, the
PHY ignores any fair requests if it asserts the receive state while the link is requesting the bus. When the link finds
the CTL terminals in a receive state, the link reissues the bus request transfer one clock cycle after the next interface
idle.
To send an acknowledge, the link must issue an ImmReq request during the reception of the packet addressed to
it. This is required because the delay from end-of-packet to acknowledge requests adds directly to the minimum delay
every PHY must wait after every packet to allow an acknowledge to occur. After the packet ends, the PHY immediately
takes control of the bus and grants the bus to the link. If the header cyclic redundancy check (CRC) of the packet turns
out to be bad, the link releases the bus immediately. The link cannot use this grant to send another type of packet.
To ensure this, the link must wait 160 ns after the end of the received packet to allow the PHY to grant it the bus for
the acknowledgement, and then the link releases the bus and proceeds with another request.
Although improbable, it is conceivable that two separate nodes can believe that an incoming packet is intended for
them. The nodes then issue an ImmReq request before checking the CRC of the packet. Since both PHYs seize
control of the bus at the same time, a temporary, localized collision of the bus occurs. As soon as the two nodes check
the CRC, the mistaken node drops its request and the false line is removed. The only side effect is the loss of the
intended acknowledgement packet (this is handled by the higher-layer protocol).
Once the link issues an immediate, fair, or urgent request for access to the bus it cannot issue another request until
the PHY indicates a lost (incoming packet) or won (transmit) signal. The PHY ignores new requests while a previous
request is pending.
6.1.2
Read/Write Requests
For read requests (see Table 6
–
6), the PHY returns the contents of the addressed register at the next opportunity
through a status transfer. For write requests, the PHY takes the value in the data field (see Table 6
–
7) of the transfer
and loads it into the addressed register as soon as the transfer is complete. When the status transfer is interrupted
by an incoming packet, the PHY continues to attempt the transfer of the requested register until it is successful.
6.1.3
Status
When the PHY has status information to transfer to the link, it initiates a status transfer. The PHY waits until the
interface is idle to perform the transfer. The PHY initiates the transfer by asserting status (01) on the CTL terminals,
along with the first two bits of status information on D0 and D1. The PHY maintains CTL status for the duration of the
status transfer. The PHY can temporarily halt a status transfer by asserting something other than status on the CTL
terminals. This is done in the event that a packet arrives before the status transfer completes. There must be at least
one idle cycle between consecutive status transfers.
The PHY normally sends only the first 4 bits of status to the link. These bits are status flags that are needed by link
state machines. The PHY sends an entire status packet to the link after a request transfer that contains a read request.
The definition of the bits in the status transfer are shown in Table 6
–
9 (also see Table 3
–
1 and Table 6
–
6). Status
transfer timing is shown in Figure 6
–
3.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TSB14AA1I | FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) |
| TSB14AA1T | FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) |
| TSB14C01MHV | IC APEX 20KE FPGA 160K 484-FBGA |
| TSB14C01HV | 5-V IEEE 1394-1995 BACKPLANE TRANSCEIVER/ARBITER |
| TSB21LV03MHV | IC APEX 20KE FPGA 200K 484-FBGA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TSB14AA1A | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:3.3 V IEEE 1394-1995 BACKPLANE PHY |
| TSB14AA1AI | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:3.3 V IEEE 1394-1995 BACKPLANE PHY |
| TSB14AA1AIPFB | 功能描述:1394 接口集成電路 IEEE139419953.3V1prt 50/100Mbps BkplnPHY RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 類型:Link Layer Controller 工作電源電壓: 封裝 / 箱體:LQFP 封裝:Tray |
| TSB14AA1AIPFBG4 | 功能描述:1394 接口集成電路 3.3V 1-port 50/100 Mbps Backplane PHY RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 類型:Link Layer Controller 工作電源電壓: 封裝 / 箱體:LQFP 封裝:Tray |
| TSB14AA1APFB | 功能描述:1394 接口集成電路 3.3V 1-port 50/100 Mbps Backplane PHY RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 類型:Link Layer Controller 工作電源電壓: 封裝 / 箱體:LQFP 封裝:Tray |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。