- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373920 > AD7854L (Analog Devices, Inc.) 12-Bit Sampling ADC(單電源,200kSPS 12位采樣A/D轉換器) PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | AD7854L |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | 12-Bit Sampling ADC(單電源,200kSPS 12位采樣A/D轉換器) |
| 中文描述: | 12位采樣ADC(單電源,速度高達200ksps的12位采樣的A / D轉換器) |
| 文件頁數: | 15/28頁 |
| 文件大小: | 268K |
| 代理商: | AD7854L |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁當前第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁
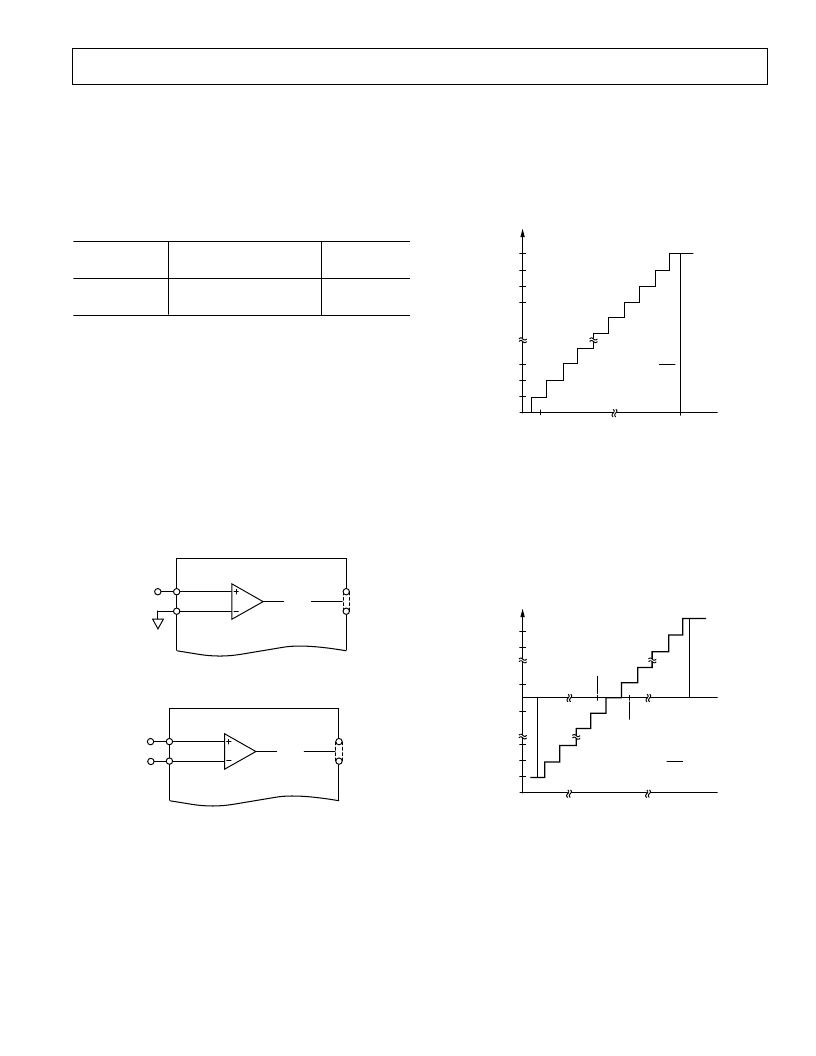
AD7854/AD7854L
REV. 0
–15–
T ransfer Functions
For the unipolar range the designed code transitions occur mid-
way between successive integer LSB values (i.e., 1/2 LSB,
3/2 LSBs, 5/2 LSBs . . . FS – 3/2 LSBs). T he output coding is
straight binary for the unipolar range with 1
LSB = FS
/4096
=
3.3
V/
4096
=
0.8
mV
when
V
REF
= 3.3
V
. T he ideal input/
output transfer characteristic for the unipolar range is shown in
Figure 14.
OUTPUT
CODE
111...111
111...110
111...101
111...100
000...011
000...010
000...001
000...000
0V 1LSB
V
IN
= (AIN(+) – AIN(–)), INPUT VOLTAGE
+FS –1LSB
1LSB =
FS
4096
Figure 14. AD7854/AD7854L Unipolar Transfer
Characteristic
Figure 13 shows the AD7854/AD7854L’s
±
V
REF
/2 bipolar ana-
log input configuration. AIN(+) cannot go below 0 V, so for the
full bipolar range, AIN(–) should be biased to at least +V
REF
/2.
Once again the designed code transitions occur midway between
successive integer L SB values. T he output coding is twos
complement with 1
LSB =
4096
=
3.3
V
/4096
=
0.8
mV
. T he
ideal input/output transfer characteristic is shown in Figure 15.
OUTPUT
CODE
111...111
111...110
111...101
111...100
000...011
000...010
000...001
000...000
V
IN
= (AIN(+) – AIN(–)), INPUT VOLTAGE
1LSB =
FS
4096
0V
(V
REF
/2) – 1LSB
(V
REF
/2) + 1 LSB
V
REF
/2
+ FS – 1LSB
FS = V
REF
V
Figure 15. AD7854/AD7854L Bipolar Transfer Characteristic
Input Ranges
T he analog input range for the AD7854/AD7854L is 0 V to
V
REF
in both the unipolar and bipolar ranges.
T he only difference between the unipolar range and the bipolar
range is that in the bipolar range the AIN(–) should be biased
up to at least +V
REF
/2 and the output coding is twos comple-
ment (see T able V and Figures 14 and 15).
T able V. Analog Input Connections
Analog Input
Range
Input Connections
AIN(+)
Connection
Diagram
AIN(–)
0 V to V
REF1
±
V
REF
/2
2
V
IN
V
IN
AGND
V
REF
/2
Figure 12
Figure 13
NOT ES
1
Output code format is straight binary.
2
Range is
±
V
REF
/2 biased about V
REF
/2. Output code format is twos complement.
Note that the AIN(–) pin on the AD7854/AD7854L can be bi-
ased up above AGND in the unipolar mode, or above V
REF
/2 in
bipolar mode if required. T he advantage of biasing the lower
end of the analog input range away from AGND is that the ana-
log input does not have to swing all the way down to AGND.
T hus, in single supply applications the input amplifier does not
have to swing all the way down to AGND. T he upper end of the
analog input range is shifted up by the same amount. Care must
be taken so that the bias applied does not shift the upper end of
the analog input above the AV
DD
supply. In the case where the
reference is the supply, AV
DD
, the AIN(–) should be tied to
AGND in unipolar mode or to AV
DD
/2 in bipolar mode.
. . .
AIN(+)
AIN(–)
V
IN
= 0 TO V
REF
TRACK AND HOLD
AMPLIFIER
DB0
DB11
STRAIGHT
BINARY
FORMAT
AD7854/AD7854L
Figure 12. 0 to V
REF
Unipolar Input Configuration
2’S
COMPLEMENT
FORMAT
V
REF
/2
. . .
AIN(+)
AIN(–)
V
IN
= 0 TO V
REF
TRACK AND HOLD
AMPLIFIER
DB0
DB11
AD7854/AD7854L
Figure 13.
±
V
REF
/2 about V
REF
/2 Bipolar Input Configuration
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7854 | 12-Bit Sampling ADC(單電源,200kSPS 12位采樣A/D轉換器) |
| AD7858LARS | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC |
| AD7858BN | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC |
| AD7858BR | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC |
| AD7858AN | 3 V to 5 V Single Supply, 200 kSPS 8-Channel, 12-Bit Sampling ADC |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| AD7854LAQ | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:12 BIT SINGLE CHANNEL PARALLEL ADC I.C. - Bulk |
| AD7854LAR | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:ADC Single SAR 100ksps 12-bit Parallel 28-Pin SOIC W 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:12-BIT SINGLE CHANNEL PARALLEL ADC I.C. - Bulk |
| AD7854LAR-REEL | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:ADC Single SAR 100ksps 12-bit Parallel 28-Pin SOIC W T/R 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:ADC SGL SAR 100KSPS 12-BIT PARALLEL 28SOIC W - Tape and Reel |
| AD7854LARS | 功能描述:IC ADC 12BIT PARALLEL LP 28-SSOP RoHS:否 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 數據采集 - 模數轉換器 系列:- 產品培訓模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標準包裝:2,500 系列:- 位數:12 采樣率(每秒):3M 數據接口:- 轉換器數目:- 功率耗散(最大):- 電壓電源:- 工作溫度:- 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:SOT-23-6 供應商設備封裝:SOT-23-6 包裝:帶卷 (TR) 輸入數目和類型:- |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。