- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄373970 > AD9886KS-140 (ANALOG DEVICES INC) Analog Interface for Flat Panel Displays PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | AD9886KS-140 |
| 廠商: | ANALOG DEVICES INC |
| 元件分類: | 消費家電 |
| 英文描述: | Analog Interface for Flat Panel Displays |
| 中文描述: | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PQFP160 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, MQFP-160 |
| 文件頁數: | 26/32頁 |
| 文件大小: | 248K |
| 代理商: | AD9886KS-140 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁當前第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁
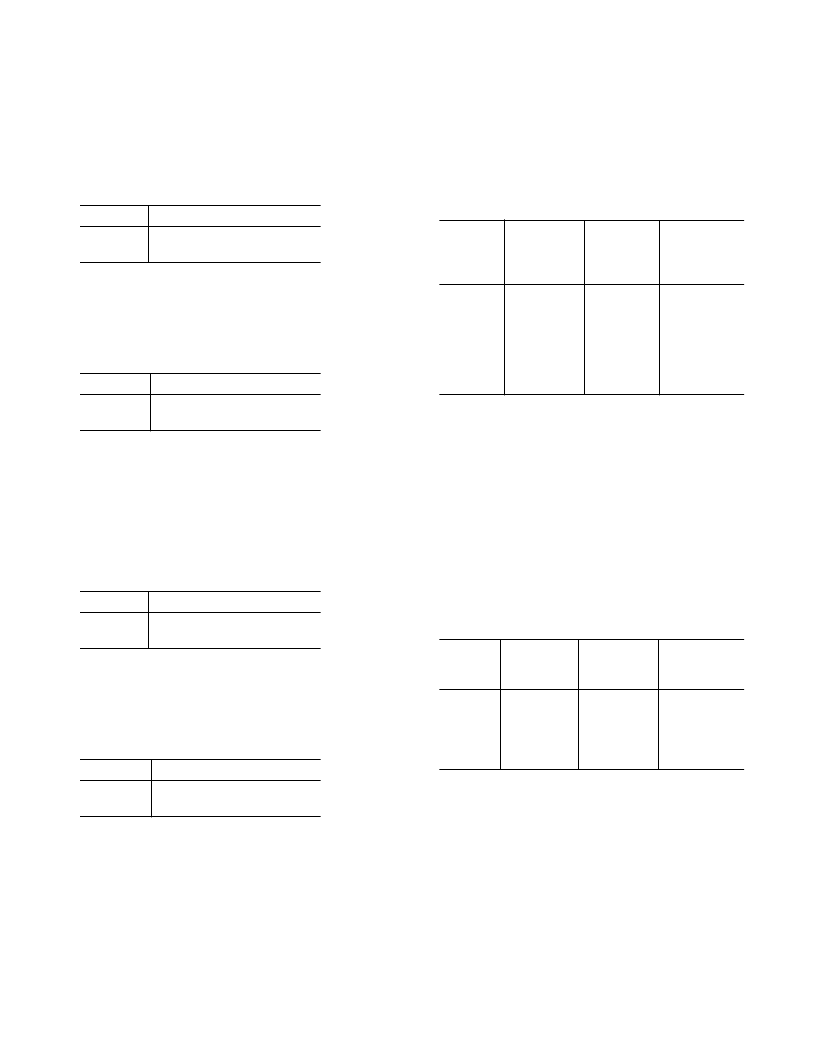
REV. 0
AD9886
–26–
SYNC DETECTION AND CONTROL
11
7
Analog Interface HSYNC Detect
This bit is used to indicate when activity is detected on
the HSYNC input pin (Pin 82). If HSYNC is held high or
low, activity will not be detected.
Table XXVI. HSYNC Detection Results
Detect
Function
0
1
No Activity Detected
Activity Detected
Figure 38 shows where this function is implemented.
6
Analog Interface Sync-on-Green Detect
This bit is used to indicate when sync activity is detected
on the Sync-on-Green input pin (Pin 108).
11
Table XXVII. Sync-on-Green Detection Results
Detect
Function
0
1
No Activity Detected
Activity Detected
Figure 38 shows where this function is implemented.
Warning: If no sync is present on the green video input,
normal video may still trigger activity.
5
Analog Interface VSYNC Detect
This bit is used to indicate when activity is detected on
the VSYNC input pin (Pin 81). If VSYNC is held high or
low, activity will not be detected.
11
Table XXVIII. VSYNC Detection Results
Detect
Function
0
1
No Activity Detected
Activity Detected
Figure 38 shows where this function is implemented.
4
Digital Interface Clock Detect
This bit is used to indicate when activity is detected on
the digital interface clock input.
11
Table XXIX. Digital Interface Clock Detection Results
Detect
Function
0
1
No Activity Detected
Activity Detected
The sync processing block diagram shows where this
function is implemented.
3
Active Interface
This bit is used to indicate which interface should be
active, analog or digital. It checks for activity on the
analog interface and for activity on the digital interface,
then determines which should be active according to
Table XXX. Specifically, analog interface detection is
determined by OR-ing Bits 7, 6, and 5 in this register.
Digital interface detection is determined by Bit 4 in this
11
register. If both interfaces are detected, the user can
determine which has priority via Bit 6 in register 12H.
The user can override this function via Bit 7 in Register
12H. If the override bit is set to Logic 1, then this bit will
be forced to whatever the state of Bit 6 in Register 12H is
set to.
Table XXX. Active Interface Results
Bits 7, 6,
or 5
(Analog
Detection)
Bit 4
(Digital
Detection)
Override
AI
0
0
0
Soft
Power-Down
(Seek Mode)
1
0
Bit 6 in 12H
Bit 6 in 12H
0
1
1
X
1
0
1
X
0
0
0
1
AI = 0 means Analog Interface.
AI = 1 means Digital Interface.
The override bit is in Register 12H, Bit 7.
2
AHS—Active HSYNC
This bit is used to determine which HSYNC should be
used for the analog interface, the HSYNC input or Sync-
on-Green. It uses Bits 7 and 6 in this register for inputs
in determining which should be active. Similar to the previ-
ous bit, if both HSYNC and SOG are detected the user
can determine which has priority via Bit 4 in Register
12H. The user can override this function via Bit 5 in
Register 12H. If the override bit is set to Logic 1, this
bit will be forced to whatever the state of Bit 4 in Register
12H is set to.
11
Table XXXI. Active HSYNC Results
Bit 7
(HSYNC
Detect)
Bit 6
(SOG
Detect)
Override
AHS
0
0
1
1
X
0
1
0
1
X
0
0
0
0
1
Bit 4 in 12H
1
0
Bit 4 in 12H
Bit 4 in 12H
AHS = 0 means use the HSYNC pin input for HSYNC.
AHS = 1 means use the SOG pin input for HSYNC.
The override bit is in Register 12H, Bit 5.
1
AVS—Active VSYNC
This bit is used to determine which VSYNC should be
used for the analog interface; the VSYNC input or output
from the sync separator. It uses Bit 5 in this register as the
input for determining which should be active. Similar to
the previous bit, if both HSYNC and SOG are detected
the user can determine which has priority via Bit 4 in
register 12H. The user can override this function via Bit 3
in Register 12H. If the override bit is set to Logic 1, this
bit will be forced to whatever the state of Bit 2 in Register
12H is set to.
11
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AD9898 | CCD Signal Processor with Precision Timing⑩ Generator |
| AD9898KCP-20 | CCD Signal Processor with Precision Timing⑩ Generator |
| AD9898KCPRL-20 | TVPS00RF-21-41S W/ PC CON |
| AD9901 | Ultrahigh Speed Phase/Frequency Discriminator |
| AD9901KP | Ultrahigh Speed Phase/Frequency Discriminator |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| AD9887 | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:Dual Interface for Flat Panel Displays |
| AD9887/PCB | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:INTRFC DUAL FOR FLAT PNL DISPLAYS 160MQFP - Bulk |
| AD9887A | 制造商:AD 制造商全稱:Analog Devices 功能描述:Dual Interface for Flat Panel Displays |
| AD9887A/PCB | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:INTRFC FOR FLAT PNL DISPLAY 16SOIC W - Bulk |
| AD9887AKS-100 | 制造商:Analog Devices 功能描述:Interface for Flat Panel Display 160-Pin MQFP 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:DUAL A/D INTERFACE FOR FLAT PANEL - Bulk |
發布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。