- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄371046 > MC68CK338 (Motorola, Inc.) Highly Integrated, Low-Power, 32-Bit Microcontroller PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | MC68CK338 |
| 廠商: | Motorola, Inc. |
| 元件分類: | 32位微控制器 |
| 英文描述: | Highly Integrated, Low-Power, 32-Bit Microcontroller |
| 中文描述: | 高度集成,低功耗,32位微控制器 |
| 文件頁數: | 70/133頁 |
| 文件大小: | 798K |
| 代理商: | MC68CK338 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁當前第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁
MOTOROLA
70
MC68CK338
MC68CK338TS/D
CPTQP[3:0] — Completed Queue Pointer
CPTQP[3:0] points to the last command executed. It is updated when the current command is complete.
When the first command in a queue is executing, CPTQP[3:0] contains either the reset value ($0) or a
pointer to the last command completed in the previous queue.
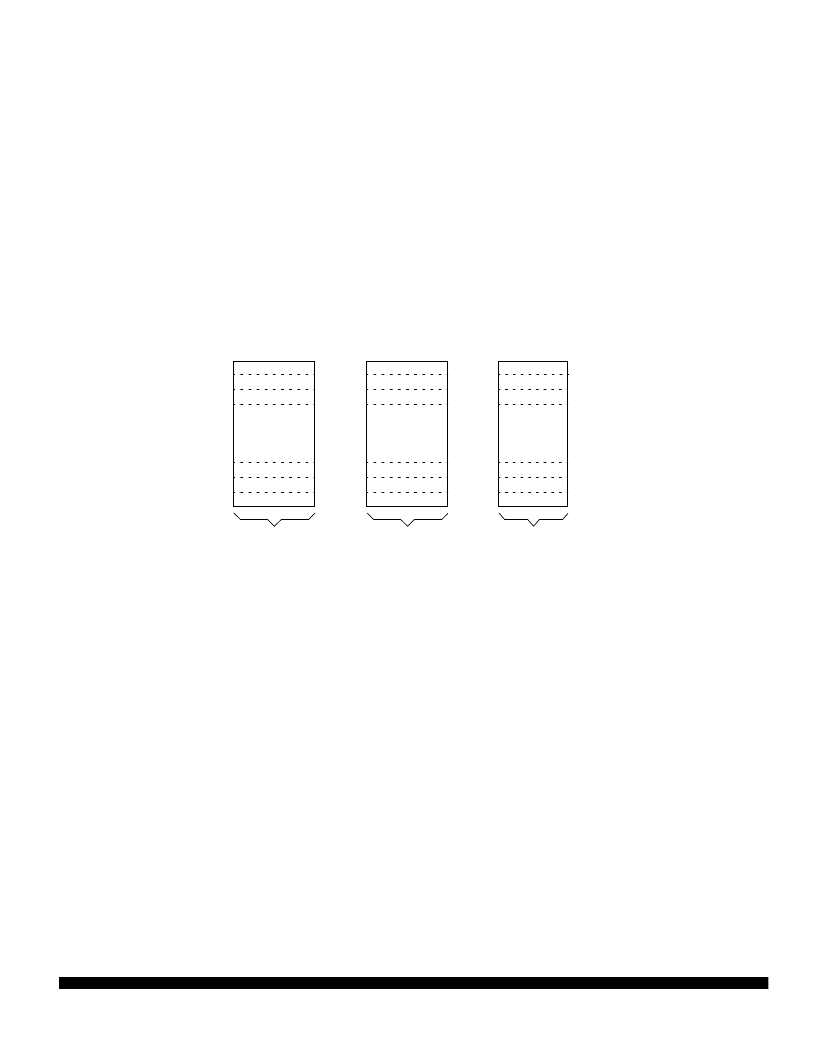
5.5.3 QSPI RAM
The QSPI contains an 80-byte block of dual-access static RAM that is used by both the QSPI and the
CPU. The RAM is divided into three segments: receive data, transmit data, and command control data.
Receive data is information received from a serial device external to the MCU. Transmit data is infor-
mation stored by the CPU for transmission to an external peripheral. Command control data is used to
perform the transfer.
Figure 16
displays the organization of the RAM.
Figure 16 QSPI RAM
Once the CPU has set up the queue of QSPI commands and enabled the QSPI, the QSPI can operate
independently of the CPU. The QSPI executes all of the commands in its queue, sets a flag indicating
that it is finished, and then either interrupts the CPU or waits for CPU intervention. It is possible to ex-
ecute a queue of commands repeatedly without CPU intervention.
RR[0:F] —
Receive Data RAM
Data received by the QSPI is stored in this segment. The CPU reads this segment to retrieve data from
the QSPI. Data stored in receive RAM is right-justified. Unused bits in a receive queue entry are set to
zero by the QSPI upon completion of the individual queue entry. The CPU can access the data using
byte, word, or long-word addressing.
$YFFD00
The CPTQP[3:0] value in SPSR shows which queue entries have been executed. The CPU uses this
information to determine which locations in receive RAM contain valid data before reading them.
TR[0:F] —
Transmit Data RAM
Data that is to be transmitted by the QSPI is stored in this segment. The CPU usually writes one word
of data into this segment for each queue command to be executed.
$YFFD20
QSPI RAM MAP
RECEIVE
RAM
TRANSMIT
RAM
500
51E
520
53E
WORD
540
54F
COMMAND
RAM
BYTE
WORD
RR0
RR1
RR2
RRD
RRE
RRF
TR0
TR1
TR2
TRD
TRE
TRF
CR0
CR1
CR2
CRD
CRE
CRF
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68EC060 | 32-Bit Microprocessors.(32位微處理器) |
| MC68EN360RC25V | QUad Integrated Communications Controller Users Manual |
| MC68EN360CFE25 | QUad Integrated Communications Controller Users Manual |
| MC68EN360FE25 | AC 4C 4#12 PIN PLUG 023 |
| MC68EN360FE25V | QUad Integrated Communications Controller Users Manual |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68CK338CPV14 | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC68CK338CPV14B1 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:32-Bit Modular Microcontroller |
| MC68CM16Z1 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:M68HC16Z Series |
| MC68CM16Z1CFC16 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:M68HC16Z Series |
| MC68CM16Z1CPV16 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:M68HC16Z Series |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。